Credit: AI-generated image (disclaimer)
Domesticated chickens in the United States alone produce more than 2 billion pounds of feathers annually. Those feathers have long been considered a waste product, especially when contaminated with blood, feces or bacteria that can prove hazardous to the environment.
Nebraska's Yiqi Yang is among a growing cadre of researchers looking to transform those feathers into fibers that find a place in natural fabrics. In that vein, Yang and his Husker colleagues are devising and testing methods to improve the properties of feather-derived fibers.
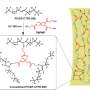
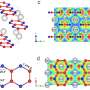
Those methods include cross-linking: chemically bonding long protein chains—including keratin, a water-resistant protein of feathers—to bolster the performance of the resulting fibers and fabrics. But that performance must still improve, and unwanted side effects of cross-linking be resolved, before feathers emerge as a greener alternative to petroleum-based materials—polyester, nylon—currently dominating the market.
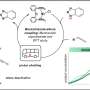
In a recent study, Yang's team experimented with a cross-linking class known as saccharide aldehydes. By modifying the molecular structure and concentration of the aldehydes, the team developed keratin fibers substantially stronger than those produced via another popular cross-linker, citric acid.
Those fibers possessed 90 percent of wool's strength after long-term immersion in water and 120 percent of wool's strength under dry conditions. Importantly, those fibers retained their color and boasted a capacity to absorb dyes that far exceeded that of other cross-linked, keratin-based fibers. The production process also yielded none of the toxic formaldehyde that has previously hounded cross-linking processes involving aldehydes.
With further improvements, the team estimates that chicken feather-derived fibers could ultimately reduce the U.S. market share of petroleum-based fibers by 10 percent (from 70 percent to 60 percent)—while putting to use an overlooked waste product of the food industry. Also, given the low cost of feathers, keratin-based fibers would likely cost less than wool, Yang said.
More information: Bingnan Mu et al, Pilot-scale spinning and sucrose-tetra-aldehydes-crosslinking of feather-derived protein fibers with improved mechanical properties and water resistance, Sustainable Materials and Technologies (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00367
Provided by University of Nebraska-Lincoln