Last update:
Soft Matter news

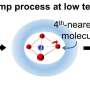
Self-organization in action: Exploring Abrikosov clusters in a liquid crystal droplet
Science often surprises us with its ability to connect seemingly unrelated phenomena. Have you ever stopped to marvel at how nature arranges itself into intricate patterns, like the spirals of a sunflower or the crystals ...

New method discovered for controlling molecular patterns on liquid droplets
A team of researchers has uncovered a previously unknown phenomenon that could improve the way we design materials at the molecular level. By unlocking a transformation between two types of structural defects on the surface ...
Soft Matter
Dec 2, 2024
1
44

3D-printed particles propel themselves across the surface of a fluid
A small team of physicists at the University of Amsterdam has demonstrated the ability of 3D-printed particles to propel themselves across the surface of a fluid, given the right fuel. The group has posted a paper describing ...

Tiny rotating particles create vorticity in viscous fluids, yielding fascinating new behaviors
Vorticity, a measure of the local rotation or swirling motion in a fluid, has long been studied by physicists and mathematicians. The dynamics of vorticity is governed by the famed Navier-Stokes equations, which tell us that ...

How tiny droplets can deform ice: Findings show potential for cryopreservation and food engineering
When water freezes slowly, the location where water turns into ice—known as the freezing front—forms a straight line. Researchers from the University of Twente showed how droplets that interact with such a freezing front ...
General Physics
Nov 25, 2024
0
25

Theoretical model explains the anomalous properties of water in extreme conditions
Water, a molecule essential for life, has unusual properties—known as anomalies—that define its behavior. However, there are still many enigmas about the molecular mechanisms that would explain the anomalies that make ...
Soft Matter
Nov 14, 2024
0
76

Fluids thicken at the speed of light: A new theory extends Einstein's relativity to real fluids
The theory of special relativity is rife with counterintuitive and surprising effects, the most famous of which are length contraction and time dilation. If an object travels at a relative speed, which is a non-negligible ...

Experiment reveals how Earth's magnetic field influences flow in planet's core
A trio of physicists, two with Coventry University, in the U.K., and the third with Laboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques Intenses, in France, has demonstrated how Earth's magnetic field may be influencing internal ...

The secrets of baseball's magic mud: Study quantifies its properties to show it's not simply a superstition
The unique properties of baseball's famed "magic" mud have never been scientifically quantified—until now. In a paper in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School ...
General Physics
Nov 4, 2024
1
175

New image recognition technique for counting particles provides diffusion information
A team of scientists have invented a technique to determine the dynamics of microscopic interacting particles by using image recognition to count the number of particles in an imaginary box. By changing the size of the observation ...

Study finds optimal standing positions in airport smoking lounges
While many smoking rooms in U.S. airports have closed in recent years, they are still common in other airports around the world. These lounges can be ventilated, but how much does it actually help the dispersion of smoke?
General Physics
Oct 29, 2024
0
50

Scientists demonstrate precise control over artificial microswimmers using electric fields
In a new study in Physical Review Letters, scientists have demonstrated a method to control artificial microswimmers using electric fields and fluid flow. These microscopic droplets could pave the way for targeted drug delivery ...

Investigating the flow of fluids with non-monotonic, 'S-shaped' rheology
Water and oil, and some other simple fluids, respond in the same way to all levels of shear stress. These are termed Newtonian fluids, and their viscosity is constant for all stresses although it will vary with temperature. ...
Soft Matter
Oct 28, 2024
0
1

Key role of structural defects in amorphous solid deformation uncovered
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Pune and the CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory (NCL) Pune have shown that the macroscopic deformation of amorphous solids is controlled by structural ...
Condensed Matter
Oct 18, 2024
0
54

A look into cloudy liquids: New method makes the expansion of turbid drops in water visible
When driving though a bank of fog, car headlights are only of limited help as the light is scattered by the water particles suspended in the air. The situation is similar when you try to observe the inside of a drop of milk ...
Soft Matter
Oct 17, 2024
0
17

Scientists achieve unprecedented control of active matter
An international research team led by Brandeis University has achieved a major breakthrough in the field of active matter physics, as detailed in a study published this week in Physical Review X. This pioneering research ...
Soft Matter
Oct 4, 2024
0
138

Ocean waves grow way beyond known limits, new research finds
Scientists have discovered that ocean waves may become far more extreme and complex than previously imagined.
General Physics
Sep 18, 2024
5
264

Beneath the brushstrokes, van Gogh's sky is alive with real-world physics
Vincent van Gogh's painting "The Starry Night" depicts a swirling blue sky with yellow moon and stars. The sky is an explosion of colors and shapes, each star encapsulated in ripples of yellow, gleaming with light like reflections ...
Soft Matter
Sep 17, 2024
0
66

Science fair project leads to new research explaining the glugging effect
As Rohit Velankar, now a senior at Fox Chapel Area High School, poured juice into a glass, he could feel that the rhythmic "glug, glug, glug" was flexing the walls of the carton.
General Physics
Sep 10, 2024
0
52

Researchers make sound waves travel in one direction only, with implications for electromagnetic wave technology
Researchers at ETH Zurich have managed to make sound waves travel only in one direction. In the future, this method could also be used in technical applications with electromagnetic waves.
General Physics
Sep 6, 2024
0
813
More news

Scientists characterize shale cap rocks at tiny scales

Modeling a right royal butterfly effect
Other news

Unexpected shifts in cell populations revise understanding of aging process

Mathematician solves the moving sofa problem

Warm Saturn-sized exoplanet discovered with TESS

Scientists examine how roasting affects the perfect brew

Universal barcodes unlock fast-paced small molecule synthesis

Discovery cracks code for how nature's microbes build antibiotics

Supramolecular sorting machine separates aromatic and aliphatic compounds