This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Artificial nanomagnets inspire mechanical system with memory capability
An international research team including Los Alamos National Laboratory and Tel Aviv University has developed a unique, mechanical metamaterial that, like a computer following instructions, can remember the order of actions performed on it. Named Chaco, after the archaeological site in northern New Mexico, the new metamaterial offers a route to applications in memory storage, robotics, and even mechanical computing.
The research has been published in Nature Communications.
"If you pull a rubber band and then twist it, you get the same result as if you had twisted and then pulled it. Ordinary materials respond in the same way to a sequence of mechanical manipulations regardless of their order," said Cristiano Nisoli, scientist at Los Alamos.
"However, Chaco exhibits history-dependent behavior and remembers past operations. That memory is typical of magnetic rather than mechanical systems; we explicitly designed Chaco as the mechanical analog of a nano-magnet, called Shakti. Our idea was that Chaco could inherit magnetic memory properties typically absent in mechanics."
Design inspired by magnetic frustration
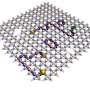
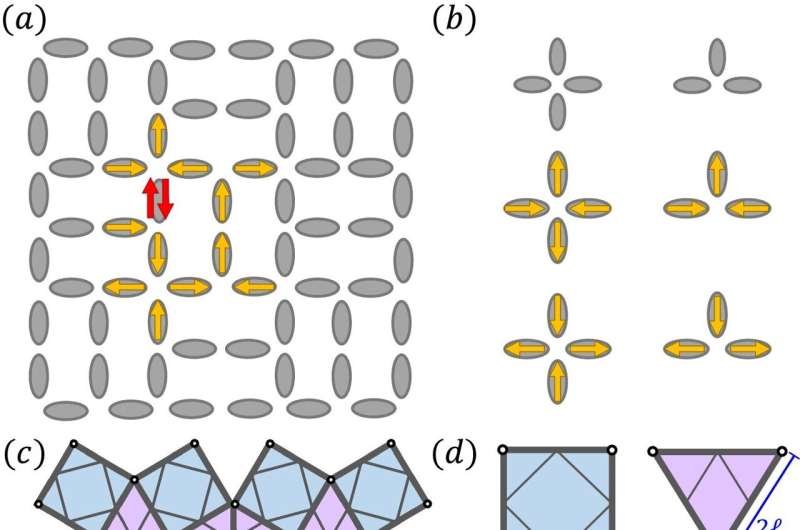
The concept of frustration, typical of exotic magnetic systems, inspired Chaco's design and underpins its memory properties. Magnets can be prevented from reaching a simple, ordered state by geometric frustration if their magnetic moments are strategically architected. Similarly, Chaco's three-dimensional building blocks are arranged in incompatible ways that prevent them from easily settling into an ordered, low-energy configuration.
"This arrangement generates a manifold of internal states, into which memory can be encoded," said Chaviva Sirote-Katz, doctoral student at Tel Aviv University.
Chaco was designed at the Theoretical division at Los Alamos and realized at Tel Aviv University. Nisoli proposed the early design by drawing on his experience in the design of frustrated artificial nanomagnets. Carl Merrigan and Yair Shokef, from Tel Aviv University, finalized the design while visiting the Center for Nonlinear Studies at Los Alamos. The group had realized that the mathematical underpinning of magnetic frustration could carry over to meta-mechanics, with similar exotic phenomenology.
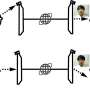
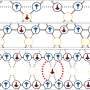
How does Chaco recognize a sequence of actions? The key is the material's non-Abelian nature, meaning that the order of operations is essential to the material's response.
"This material is like a mechanical memory storage device that can remember a sequence of inputs," said Dor Shohat, a doctoral student at Tel Aviv University in the group of Yoav Lahini.
"Each of its mechanical building blocks has two stable states, just like a single bit of magnetic memory. Flipping two units within the material may lead to one final state, but flipping those two units in the reverse order would lead to a different final state."
Encoding information in the sequence of actions
The researchers used this capability to encode information in the sequence of actions. Observing the final state of the material retrieves the information.
"The field of meta-mechanics has been promising new smart materials by design," Nisoli said. "In the Theoretical division, we had been doing something similar by designing new nanomagnets. And now, by imbuing mechanical materials with the exotic properties and functionalities associated with magnets, we have opened a new design direction in meta-mechanics."
More information: Chaviva Sirote-Katz et al, Emergent disorder and mechanical memory in periodic metamaterials, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47780-w
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Los Alamos National Laboratory