This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study finds active matter and shear flows share thinning behaviors
According to a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a research team led by Professor Xu Ning from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has found that active matter and shear flows share similar thinning behaviors in self-propulsion and shear forces.
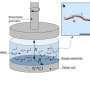
Active substances can spontaneously move by consuming their own or environmental energy, with biological organisms being typical representatives. Since active substances are non-equilibrium systems, a large number of active substance individuals gathering together will exhibit very rich and peculiar collective motion behaviors, which is currently a hot topic in many related disciplines.
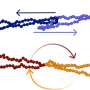
The team proposed a new viewpoint that the collective motion behavior of active matter was similar to sheared systems. Despite significant differences in energy input methods between active matter and shear systems, the team was among the first internationally to compare the two systems, finding direct evidence of potential correlations.
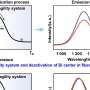
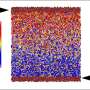
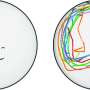
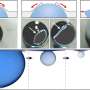
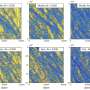
The team found that the viscosity changes in active matter with active force resembled those in sheared systems with shear stress, both stemming from the micro-mechanism of breaking up percolating particle clusters; and that the faster the clusters broke, the more dramatically the viscosity dropped.
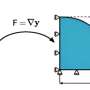
For ordinary Newtonian fluids, shear action only caused molecules to tend to align along the shear flow direction, forming percolating clusters that remain stable; thus, viscosity remained unaffected by shear stress.
However, the addition of active matter changed this scenario. Since the direction of active force could randomly deviate, it endowed active matter with the ability to break percolating clusters, leading to a decrease in solution viscosity.
This work offers a possible explanation for the "superfluid"-like phenomena caused by E. coli and further substantiates the evidence of potential links between active matter and sheared systems.
More information: Ruoyang Mo et al, Thinning by cluster breaking: Active matter and shear flows share thinning mechanisms, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2318917121
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by University of Science and Technology of China