Wearable "skin" and biosensor. Credit: Monash University
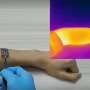
A new ultra-thin skinpatch with nanotechnology able to monitor 11 human health signals has been developed by researchers at Monash University.
Researchers from the Faculty of Engineering and Faculty of Information Technology combined nanotechnology and artificial intelligence to bring machines one step closer to communicating with the human body.
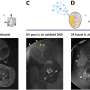
Using specialized algorithms, personalized Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology can now disentangle multiple body signals, understand them and make a decision on what to do next.
Published recently in Nature Nanotechnology, the research could change how we deliver remote health care and be the future of personal alarms and communications devices.
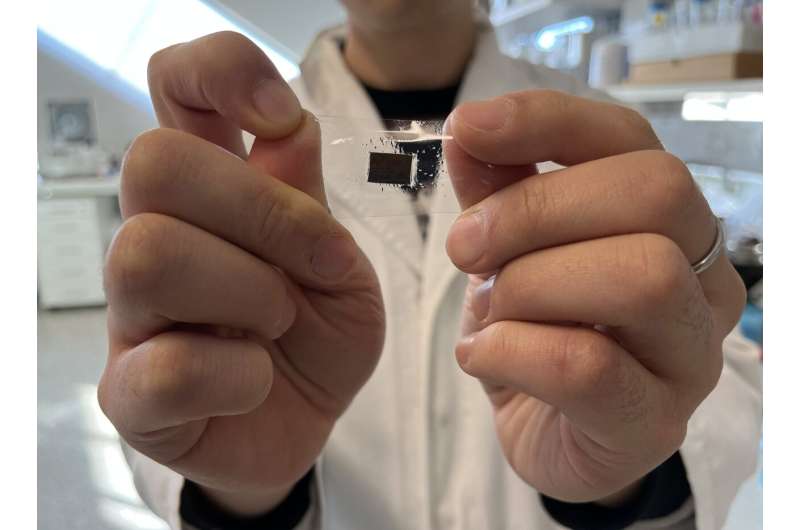
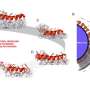
Worn on the neck, lead researcher Professor Wenlong Cheng said the ultra-thin wearable patch has three layers, measuring speech, neck movement and touch. It also measures breathing and heart rates.
Prof Zongyuan Ge demonstrating interaction through the skinpatch. Credit: Monash University
"Emerging soft electronics have the potential to serve as second-skin-like wearable patches for monitoring human health vitals, designing perception robotics and bridging interactions between natural and artificial intelligence," Professor Cheng said.
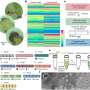
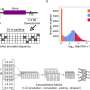
Associate Professor Zongyuan Ge, from the Faculty of Information Technology, is part of the Monash team to have developed a frequency/amplitude-based neural network called Deep Hybrid-Spectro, that can automatically monitor multiple biometrics from a single signal.
"As people all sound and act differently, the next step is to program and personalize the sensors using even more sophisticated algorithms so they can be tailored to individuals," Associate Professor Ge added.
The sensor is made from laminated cracked platinum film, vertically aligned gold nanowires and a percolated gold nanowire film.
Neck skin is the most sensitive skin on the body and connects up to five physiological activities associated with the human throat: speech, heartbeats, breathing, touch and neck movement.
More information: Shu Gong et al, Hierarchically resistive skins as specific and multimetric on-throat wearable biosensors, Nature Nanotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-023-01383-6
Journal information: Nature Nanotechnology
Provided by Monash University