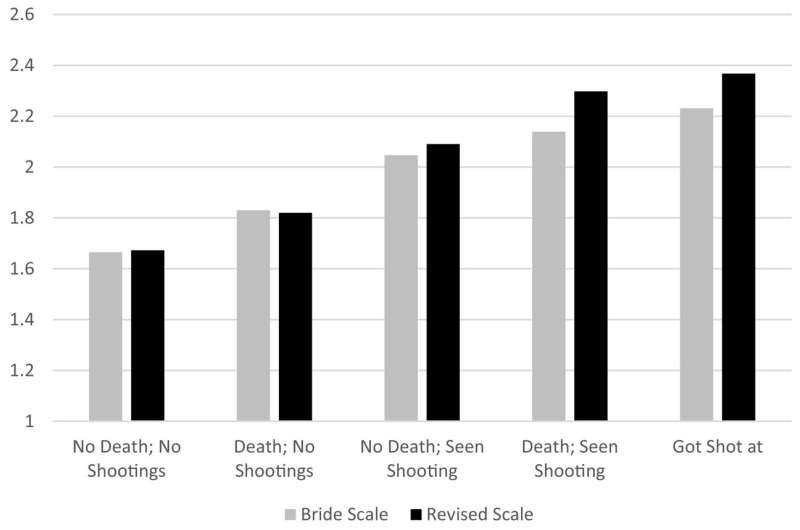
Mean STSS Score by Interventionist Traumatic Experiences. Credit: Preventive Medicine (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2022.107186
Two newly published articles by researchers at the University at Albany and Northwestern University show the extent to which civilians working to intervene in and de-escalate street violence face job-related violence themselves, as well as secondary trauma from that violence.
Increases in gun violence and homicide in recent years, along with a renewed focus on racial inequality and the social harms stemming from existing police and crime control policies, have resulted in a greater interest in community violence intervention (CVI) programs.
Civic leaders and policymakers are calling for increased investment in CVI, programs that are designed to reduce homicides and shootings by mediating gang and interpersonal conflicts, monitoring and responding to flash points for community violence, and mentoring those at highest risk of violence and connecting them to crucial social services.
CVI workers, civilians trained in violence de-escalation techniques and often steeped in the communities in which they work, have made strides in reducing violence and building connections within the neighborhoods they serve, but they also face gun violence and victimization themselves.
A landmark study conducted in 2021, co-led by David Hureau, executive director of the Hindelang Criminal Justice Research Center and assistant professor at UAlbany's School of Criminal Justice (SCJ), and Andrew Papachristos, professor of sociology at Northwestern University, found that 60 percent of Chicago CVI workers witnessed people being shot at, and nearly 20 percent were shot at themselves during work hours.
A new article published Dec. 23 in Science Advances, presents some of the key findings from that study, Violence Intervention Worker Study (VIeWS).
Hureau is lead author on the article, "Exposure to gun violence among the population of Chicago community violence interventionists," which is based on surveys from nearly the entire street outreach workforce in Chicago. The article was co-written by SCJ's Assistant Professor Theodore Wilson and Ph.D. student Hilary Jackl, along with Jalon Arthur of the violence reduction project Chicago CRED, Christopher Patterson of the Office of Firearm Violence Prevention, Illinois Department of Human Services, and Papachristos of Northwestern.
The article notes that in addition to direct exposure to gun violence, the Chicago interventionists commonly face direct exposure to death, violent death and loss of colleagues. The survey found:
- 80% of CVI workers have responded to a scene of violence before emergency services
- 74% have seen a deceased victim
- 83% have seen a shooting victim at the scene
- 25% have directly witnessed someone killed in an act of violence.
- 65% knew someone from their professional duties who was killed
- 20% knew someone through work who committed suicide
- 52% experienced the death of a client due to violence.
In a separate study, the research team examined this indirect exposure to violence, and found that Chicago CVI workers experienced symptoms of secondary traumatic stress—the stress stemming from working with traumatized populations—that were exacerbated by workplace exposure to violence that is common in the profession.
The results were published in a paper in Preventive Medicine, written by Hureau, Wilson, Papachristos and Wayne Rivera-Cuadrado, a sociology Ph.D. student at Northwestern. Using the VIeWS study, the authors found that nearly all interventionists reported at least one secondary traumatic stress indicator in the past seven days, and that workers who experienced the death of a client, witnessed a shooting, or were shot at themselves were more likely to be affected by secondary traumatic stress.
"In a moment where policymakers are seeking to invest more seriously in Community Violence Intervention strategies," Hureau said, "my hope is that this research will stimulate further interest in supporting people that do this important public safety work. Improving work conditions for community violence interventionists will ultimately lead to increased program effectiveness and healthier communities."
More information: David M. Hureau et al, Exposure to gun violence among the population of Chicago community violence interventionists, Science Advances (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq7027
David M. Hureau et al, The experience of secondary traumatic stress among community violence interventionists in Chicago, Preventive Medicine (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2022.107186
Journal information: Science Advances , Preventive Medicine
Provided by University at Albany