Scientists from the Instituto de Neurociencias CSIC-UMH in Alicante, Spain, under the supervision of Professor Angela Nieto, have discovered the molecular mechanism that ensures equilibrium in left-right signaling cascades during development for the correct leftward positioning of the heart.
Previous findings of the research group published in Nature in 2017 have shown that for the heart to move to the left from it is initial central position, it receives cells from both the left and right-hand sides of the embryo, but more cells are traveling from the right. This establishes asymmetric forces that push the heart to the left. However the question remained as to how this left-right asymmetry in cell contribution was established.
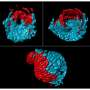
This question is answered in the work published in Developmental Cell. "We have now found that during a very short time window, a wave of small molecules called microRNAs travel all along the left-hand side of the embryo, attenuating the signals that send cells to the heart and, therefore, more cells travel from the right-hand side toward the midline, pushing the heart to the left," explains the first author of the work, Luciano Rago.
"An interesting fact is that this mechanism seems to be conserved in all vertebrates, including humans, as we found that it is present in zebrafish, chicken and mouse embryos," says Professor Nieto.
This work is an important contribution to the developmental biology field, because it explains the temporal and dynamic regulation of the main players governing organ positioning, and integrates previous knowledge and new findings in left-right determination in the embryo.
Until 2017, researchers believed that left-right asymmetry was mainly established by information coming from the left that was suppressed on the right. However, thanks to their previous work and the study published now in Developmental Cell, Professor Nieto's group report that the integration of information coming from both sides of the embryo is key to establishing the final position of the heart and its proper development.
The proper position of the heart, with its posterior pole pointing to the left, is fundamental for a correct concordance of the heart with the circulatory system. Around 50 percent of congenital malformations detected at birth in humans are heart malformations, and many of those are related to defects in heart positioning. Thus, the description of the mechanism that ensures its correct position helps to better understand cardiac malformations.
Journal information: Nature , Developmental Cell
Provided by Spanish National Research Council