Researchers decipher how an enzyme modifies the genetic material in the cell nucleus
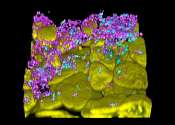
Inside the cell nucleus, the DNA molecule is found in a densely packed DNA-protein complex known as chromatin. Here the DNA is wrapped around a core of histone proteins and densely packed to form nucleosomes. The structure ...