Credit: CC0 Public Domain
Researchers from Siberian Federal University and Kirensky Institute of Physics have proposed a new design for a multimode stripline resonator. The use of such resonators allows scientists to create miniature band-pass filters with unique frequency-selective properties that are in demand by modern telecommunication systems. The main results of the study are published in Technical Physics Letters.
The rapid development and widespread use of telecommunication systems, radar systems, radio navigation and special radio equipment, along with the presence of natural sources of radio emission, has led to a significant deterioration in the electromagnetic environment. Each radio device operates in its own frequency range, while simultaneously creating radio interference for other devices. To reduce the level of interference, devices that carry out the frequency filtering of radio noise are used. Such devices, called frequency selective devices or filters, are used in radio transmitting devices to attenuate the signals emitted by them outside the main frequency band. In the receiving devices, they are used as preselectors, attenuating the level of interference coming from the antenna.
Thus, radio filters are designed to highlight electromagnetic waves lying in certain frequency ranges. Frequency bands in which the attenuation of the signal at the filter output is small are the pass bands (transparency). The remaining frequency ranges are the stop (suppression) bands.
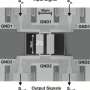
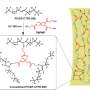
Today, filters are widely used on lumped elements—inductors and capacitors, piezoelectric and magnetostrictive filters, and filters on surface acoustic waves. However, in the microwave range, filters based on interacting electrodynamic resonators are used. Stripline resonators have a special place among a wide range of electrodynamic resonators. They consist of strip conductors usually located on dielectric substrates. Stripline resonators are characterized by high reliability, small size, low cost, and, most importantly, ease of manufacturing using modern planar integrated circuit technology.
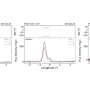
"In our work, a new design of a miniature stripline resonator on a substrate with a double-sided pattern of strip conductors was proposed. Due to the fact that several oscillation modes are used in the cavity as working, we managed not only to reduce the size of the pass band filters based on such resonators, but also to significantly improve their selective properties. The design of the filter developed by the team demonstrates the unique steepness of the slopes of the pass band and the ultra-wide high-frequency stop band, which reaches 100 dB in frequency (attenuation power decay is 10 orders of magnitude) up to a frequency five times the center frequency of the pass band. In fact, this means better selectivity than the known world analogues. And this allows us to increase the immunity to interference, increase the quality and range of information transmission, for example, in cellular and satellite communication systems, radar and radio navigation," says Aleksey Serzhantov, professor at the Department of Radio Engineering of Siberian Federal University.
More information: B. A. Belyaev et al. A Highly Selective Bandpass Filter Based on Suspended Substrate Resonators with a Two-Sided Stripline Pattern, Technical Physics Letters (2019). DOI: 10.1134/S1063785019050225
Provided by Siberian Federal University (SFU)