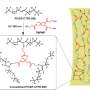
A chameleon can flexibly change its colour to match its surroundings. And a similar phenomenon can now be seen in a new class of smart materials called metamaterials. The trouble is that these metamaterials lack the ability to respond to nearby objects due to their physical characteristics. To remedy this shortcoming, Chinese physicists have developed so-called 'metashells': hollow shells made of metamaterials and capable of carrying materials in their core. The advantage is that their physical characteristics, such as permittivity—the extent to which a material can store charge within an electrical field—change with the electromagnetic properties of the material they contain. In a recent theoretical study published in The European Physical Journal B, Liujun Xu and Jiping Huang from Fudan University in Shanghai, China, describe how they have developed an entire class of these chameleon-like metashells.
Metamaterials are known for their negative refraction index, both for electromagnetic waves and other wave phenomena like sound waves. A negative index can change the direction of incoming waves dramatically and even 'bend them away'. But the permittivity of the current metamaterials—which, together with permeability, determines their refraction index—is a static property, which means they don't adapt to their environment. The metashells can help change that.
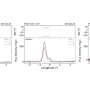
Both physicists carefully calculated the effective properties of the metashells, and managed to make these properties equal to those of the material stored inside their core. As a result, the metashells become adaptive. The authors performed theoretical analyses, which are further validated by simulations.
These intelligent metashells could become an all-purpose material to satisfy different permittivity requirements under different conditions. The next stages will focus on experimental research, and on industrial applications.
More information: Liujun Xu et al, Electrostatic chameleons: theory of intelligent metashells with adaptive response to inside objects, The European Physical Journal B (2019). DOI: 10.1140/epjb/e2019-90656-2
Journal information: European Physical Journal B
Provided by Springer