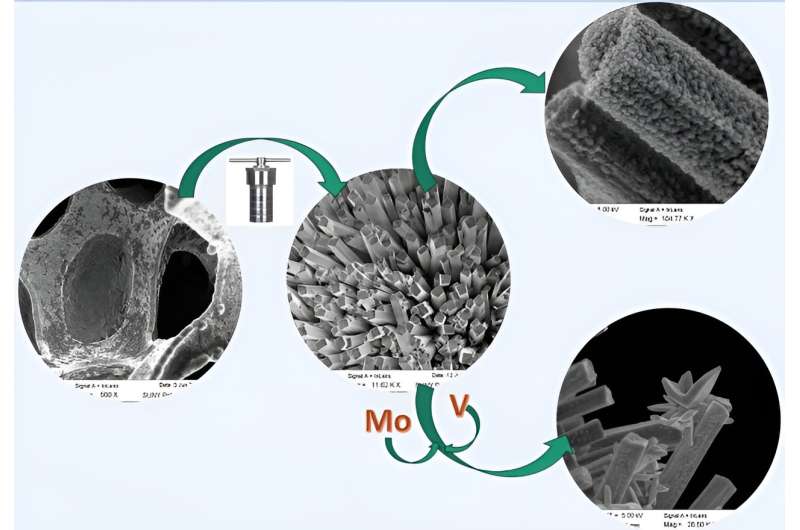
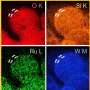
Graphical abstract. Credit: Journal of Applied Electrochemistry (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s10800-023-02064-x
SUNY Polytechnic Institute (SUNY Poly) Associate Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Technology Dr. Iulian Gherasoiu and peers have published research in the Journal of Applied Electrochemistry titled "MoVN-coated MoNi4-MoO2 nanorods as a bifunctional electrode for electrochemical water splitting."
The emerging need for clean and renewable energy drives the exploration of effective strategies to produce molecular hydrogen, Gherasoiu explains. With the assistance of highly active, non-noble metal electrocatalysts, electrolysis of water is a promising candidate to generate pure hydrogen with high efficiency.
However, this reaction takes place almost exclusively on Pt/C catalysts at the cathode which is expensive and needs to be replaced by a metal-based catalyst that is cost effective and can show a comparable HER (hydrogen evolution reaction) activity.
This research uncovers the properties of cost-effective MoVN/MoNi4-MoO2 nanorods that are synthesized using a two-step facile hydrothermal method.
The electrodes having high specific electrochemical surface area, low overpotential for both half-cell reactions (HER and OER), and negligible degradation, performed exceptionally well providing a competitive path to the fabrication of low-cost and highly effective electrodes, as a potential replacement for Pt-based electrodes, for application in commercial electrolyzers.
More information: Yamini Kumaran et al, MoVN-coated MoNi4-MoO2 nanorods as a bifunctional electrode for electrochemical water splitting, Journal of Applied Electrochemistry (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s10800-023-02064-x
Provided by Colleges of Nanoscale Science and Engineering