Credit: Environmental Pollution (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122578
Metal(loid) toxicity severely inhibits plant growth and development, thereby affecting yield and quality. It is crucial to seek favorable measures to improve plant survival under toxic metal(loid) conditions.
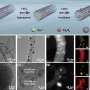
Previous studies have identified the complex mechanisms of Panax notoginseng, a traditional medicinal plant, and its responses to biotic and abiotic stress. However, the effects of nanoparticles (NPs), especially iron oxide NPs in the response of P. notoginseng to cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As) stress, have yet to be further elucidated.
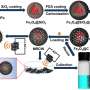
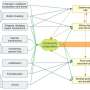
In a study published in Environmental Pollution, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) investigated the effects of Fe3O4 NPs on Panax notoginseng under Cd and As stress. By combining physiological and metabolomic analyses, the researchers examined the mechanisms of the P. notoginseng seedling response to Cd/As stress with or without foliar exposure to Fe3O4 NPs.
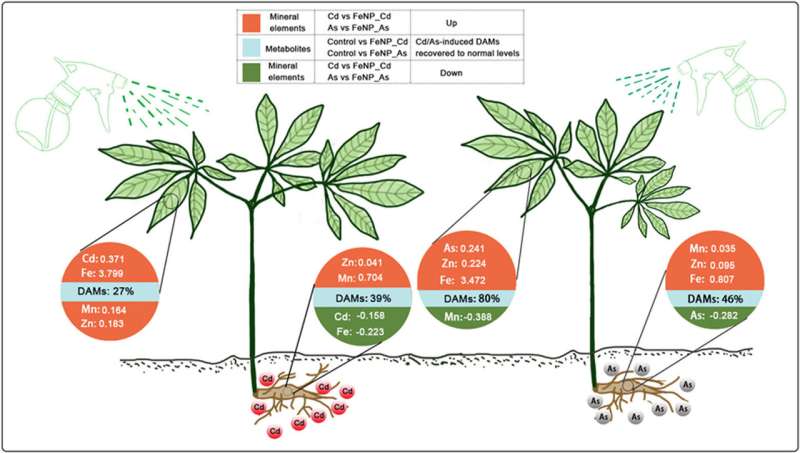
They found that Cd/As treatment severely inhibited seedling growth as indicated by the decrease in shoot fresh weight, rootlet length, and root fresh weight. By regulating ion balance, antioxidant levels and metabolic profiling, Fe3O4 NPs ameliorated Cd/As-induced growth inhibition.
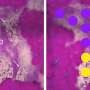
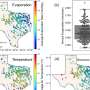
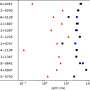
Fe3O4 NPs altered essential metabolites significantly enriched in amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, flavonoid biosynthesis, and phenylalanine metabolism, thus modulating the trade-off between plant growth and defense against metal toxicity.
More importantly, Fe3O4 NPs restored many Cd/As-induced DAMs to normal levels, further supporting that Fe3O4 NPs were beneficial for seedling growth under stress. In addition, terpenoids were significantly induced when subjected to Cd/As stress, and Fe3O4 NPs altered these key metabolites, thus affecting their potential medicinal value.
"This study suggests that metal nanoparticles can serve as nanoregulators to combat metal(loid) stress in the genuine production area of medicinal plants. They can be used to enhance potential active ingredients of medicinal plants in metal(loid)-contaminated areas," said Wan Jinpeng of XTBG.
More information: Tianquan Lu et al, Physiological and metabolomic analyses reveal that Fe3O4 nanoparticles ameliorate cadmium and arsenic toxicity in Panax notoginseng, Environmental Pollution (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122578
Journal information: Environmental Pollution
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences