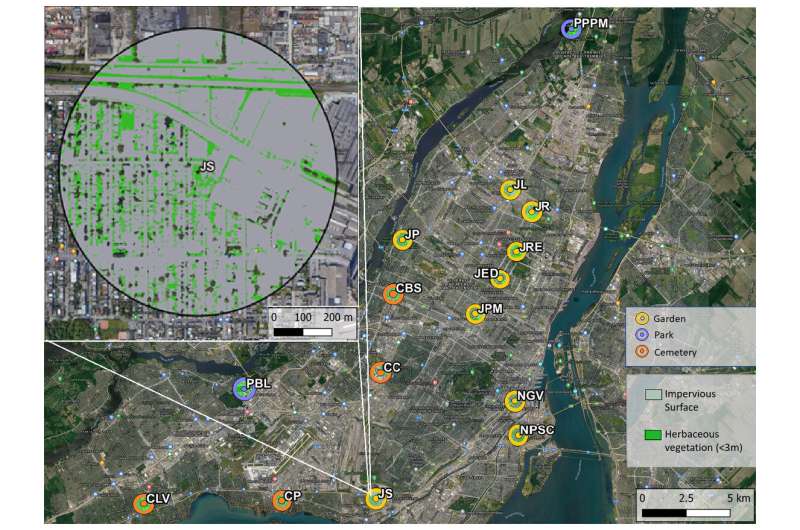
Map of study sites across the Island of Montréal, Quebec, Canada. Herbaceous vegetation was quantified as greenery under three meters in height, impervious surface was the area of pavement and built infrastructure. Top left is an enlarged view highlighting the herbaceous vegetation (bright green) and impervious surface (gray) in 500 meter buffers around each site. Abbreviated site names are adjacent to each site. Map Base layer: Google 2019, Map data: Montreal Metropolitan Community, 2011–2021. Credit: PeerJ (2023). DOI: 10.7717/peerj.14699
A new study published in PeerJ has provided insights into how western honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) in urban areas may represent a new threat to wild bee communities. On the Island of Montréal, Canada there has been a particularly large increase in beekeeping across the city.
The study examined the wild bee communities and floral resources across a gradient of honey bee abundances in urban greenspaces in 2020, and compared the bee communities at the same sites before and after the large influx of honey bees. The research found a negative relationship between urban beekeeping, pollen availability, and wild bee species richness. It also found that honey bee abundance had the strongest negative effect on small wild bee species richness.
The study found:
- Wild bee populations can fluctuate largely in space and time, however, the analyses of the bee and floral community in 2020, and the comparison to the bee community in 2013, strongly suggests a negative relationship between high-density urban beekeeping and wild bee richness.
- Urban floral communities are often dominated by exotic and cultivated plants, and native bees tend to prefer native plants, exotic bees are thought to have an advantage in urban environments
- Small bee species (ITS <2.25 mm) were influenced by the presence of managed honey bees. The analyses of the small wild bee community (57% of all wild bees sampled) showed a decline in richness with honey bee abundance across both sites and years, not seen in the large bee community.
Despite the natural spatiotemporal variation in bee community composition and the complexity of competitive interactions among bee species, the study detected a significantly negative relationship between honeybee abundance and wild bee richness. However, the study is correlative by design, and provides only indirect evidence of exploitative competition.
Negative correlations between honey bee populations and wild bee diversity cannot be interpreted as direct evidence for competitive exclusion. To complement field studies, more experimental investigations of the fitness impacts of honey bees on wild bee species over multiple years are needed to further our understanding of interspecies competition, and provide reliable estimates of the carrying capacity of cities for honey bees.
More information: Gail MacInnis et al, Decline in wild bee species richness associated with honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) abundance in an urban ecosystem, PeerJ (2023). DOI: 10.7717/peerj.14699
Journal information: PeerJ
Provided by PeerJ