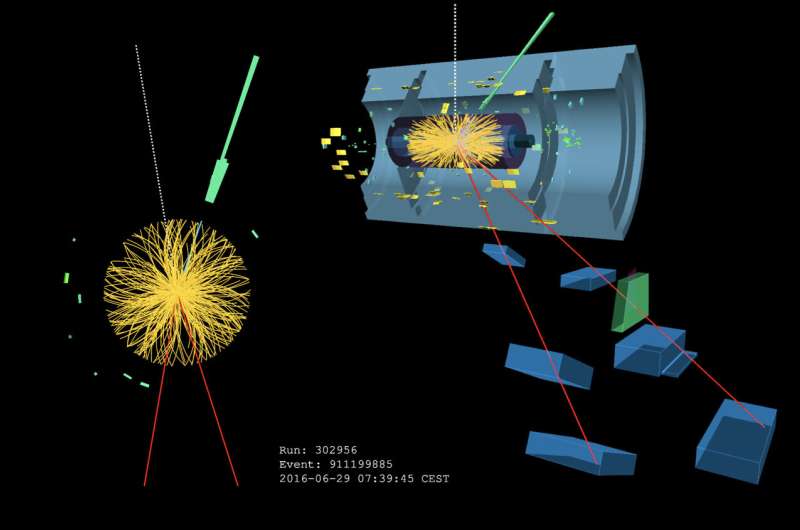
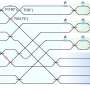
ATLAS candidate event for a W and a Z boson produced simultaneously with a longitudinal polarization. Credit: ATLAS/CERN
In the Standard Model of particle physics, the Brout-Englert-Higgs mechanism provides mass to elementary particles. While physicists are carrying out direct studies of the Higgs boson to test this mechanism, probes of other particles that have mass can also provide insight. For instance, the W and Z bosons—the carriers of the weak force—get their mass from the Higgs mechanism. This impacts their polarization, that is, the degree by which their quantum spin is aligned to a given direction. The W and Z bosons have a spin of 1 and can be longitudinally polarized as a direct consequence of their being massive—in other words, their spin can be oriented perpendicular to their direction of motion.
The simultaneous production of two W or Z bosons (or "diboson" production) allows physicists to study fundamental interactions between bosons. These rare processes have yet to be fully tested against Standard Model predictions, and studying the polarization of the produced bosons is a way to potentially unveil new physics effects. While the polarization of W and Z bosons separately has been studied since the era of the Large Electron-Positron (LEP) collider, the predecessor to the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), two such bosons produced simultaneously with a longitudinal polarization have never been observed. With the wealth of data collected during Run 2 of the LHC and innovative analysis methods, ATLAS researchers are now able to study the joint-polarization states of diboson production events.
In a new study presented at the ICHEP 2022 conference, ATLAS physicists have been able to observe events with both a W and a Z boson simultaneously polarized longitudinally for the very first time. To achieve this result, the researchers identified events containing both a W boson and a Z boson. They focused on events where the bosons transform, or "decay," into particles called leptons, as these leave the clearest signature in the ATLAS detector. The polarization of the parent bosons in such WZ events manifests itself in angular observables that have very distinct distributions for different polarization states.
However, not all of the four possible WZ joint-polarization states—longitudinal-longitudinal, longitudinal-transverse, transverse-longitudinal and transverse-transverse—are equally probable. The most interesting events, with both bosons exhibiting a longitudinal polarization, are well hidden—they represent only about 7% of all WZ events, amounting to just 1,200 of the 17,100 WZ events studied by ATLAS.
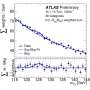
To overcome the main experimental challenges, researchers developed dedicated machine-learning algorithms to extract the fractions of the four types of joint-polarization events with a relative uncertainty of about 20%, at most. They found that the Standard Model predictions for these fractions always lie within the 95.5% confidence level region of the measurements, meaning that there is no significant tension with the theory. Researchers also found that the product of the two single-boson longitudinal polarization fractions is about 50% below the actual longitudinal-longitudinal joint-polarization fraction. This is a direct measure of the role played by correlations between the two bosons and demonstrates that the two single-boson polarizations are not independent.
This result is a fascinating look into some of the most fundamental structures of the Standard Model itself. And the feasibility of joint-polarization measurements provides new opportunities to look for new physics phenomena, targeting more specific (and rarer) processes. Building on the novel techniques developed here, physicists can now envisage the even more challenging joint-polarization measurement of the scattering of two longitudinally polarized bosons.
More information: Observation of gauge boson joint-polarisation states in W±Z production from p p collisions at √s = 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector (2022)
Provided by CERN