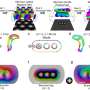
Protein structure-guided design of high-affinity PYR1-based cannabinoid sensors. a, The 19 side chains of residues in PYR1’s binding pocket targeted for double-site mutagenesis (DSM) are shown along with ABA (yellow) and HAB1’s W385 ‘lock’ residue and water network (3QN1). b, Sensor evolution pipeline. The PYR1 library was constructed by NM in two subpools, one using single-mutant oligos and another using double-mutant oligo pools. The combined pools were screened for sensors using Y2H growth selections in the presence of a ligand of interest. c, Representative screen results. The DSM library was screened for mutants that respond to the synthetic cannabinoid JWH-015 yielding five hits that were subsequently optimized by two rounds of DNA shuffling to yield PYR1JWH-015, which harbors four mutations. The yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) staining data show different receptor responses to JWH-015 by β-galactosidase activity. Credit: Nature Biotechnology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41587-022-01364-5
Scientists have modified proteins involved in plants' natural response to stress, making them the basis of innovative tests for multiple chemicals, including banned pesticides and deadly, synthetic cannabinoids.
During drought, plants produce ABA, a hormone that helps them hold on to water. Additional proteins, called receptors, help the plant recognize and respond to ABA. UC Riverside researchers helped demonstrate that these ABA receptors can be easily modified to quickly signal the presence of nearly 20 different chemicals.
The research team's work in transforming these plant-based molecules is described in a new Nature Biotechnology journal article.
Researchers frequently need to detect all kinds of molecules, including those that harm people or the environment. Though methods to do that exist, they are often costly and require complicated equipment.
"It would be transformative if we could develop rapid dipstick tests to know if a dangerous chemical, like a synthetic cannabinoid, is present. This new paper gives others a roadmap to doing that," said Sean Cutler, a UCR plant cell biology professor and paper co-author.
The problem with synthetic cannabinoids is something Cutler calls, "regulatory whack-a-mole." Because they send people to the hospital, authorities have attempted to outlaw them in this country. However, dozens of new versions emerge every year before they can be controlled.
"Our system could be configured to detect lab-made cannabinoid variations as quickly as they appear on the market," Cutler said.
The research team also demonstrated their testing system can signal the presence of organophosphates, which includes many banned pesticides that are toxic and potentially lethal to humans. Not all organophosphate pesticides are banned but being able to quickly detect the ones that are could help officials monitor water quality without more expensive testing at laboratories.
For this project, the researchers demonstrated the system in laboratory-grown yeast cells. In the future, the team would like to put the modified molecules back into plants that could serve as biological sensors. In that case, a chemical in the environment could cause leaves to turn specific colors or change temperatures.
Although the work focuses on cannabinoids and pesticides, the key breakthrough here is the ability to rapidly develop diagnostics for chemicals using a simple and inexpensive system. "If we can expand this to lots of other chemical classes, this is a big step forward because developing new tests can be a slow process," said Ian Wheeldon, study co-author and UCR chemical engineer.
This research was developed through a contract with the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center to support the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Advanced Plant Technologies (APT) program. The team included scientists from the Medical College of Wisconsin, Michigan State University, and the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center in St. Louis. This work was facilitated by chemical and biological engineer Timothy Whitehead at the University of Colorado, Boulder.
To create this system, researchers took advantage of the ABA plant stress hormone's ability to switch receptor molecules on and off. In the "on" position, the receptors bind to another protein, forming a tight complex that can trigger visible responses, like glowing. Whitehead, a collaborator on the work, used state-of-the-art computational tools to help redesign the receptors, which was critical to the success of the group's work.
"We take an enzyme that can glow in the right context and split it into two pieces. One piece on the switch, and the other on the protein it binds to," Cutler said. "This trick of bringing two things together in the presence of a third chemical isn't new. Our advance is showing we can reprogram the process to work with lots of different third chemicals."
More information: Jesús Beltrán et al, Rapid biosensor development using plant hormone receptors as reprogrammable scaffolds, Nature Biotechnology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41587-022-01364-5
Journal information: Nature Biotechnology
Provided by University of California - Riverside