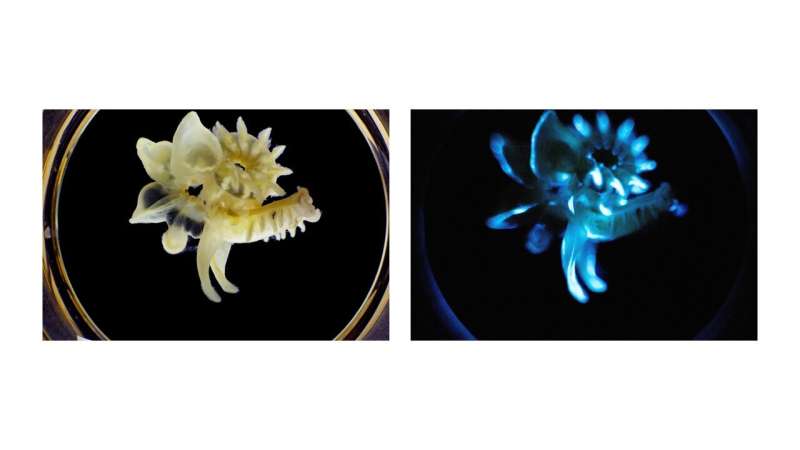
The photograph on the left shows the marine parchment tube worm (Chaetopterus sp.) under natural light. The worm is curled up, tucking its tail under its head. The image on the right shows the same worm but in the dark, capturing the blue light (bioluminescence) coming from the slime/mucus that is continuously produced by the worm when it feels threatened. Credit: David Liittschwager
When threatened, the marine parchment tube worm secretes a sticky slime that emits a unique long-lasting blue light. New research into how the worm creates and sustains this light suggests that the process is self-powered.
"The light, or bioluminescence, produced by this worm does not appear as flashes, like in most luminous organisms, but as a long-lasting glow," said Evelien De Meulenaere, Ph.D., a researcher in Dimitri Deheyn's lab at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. "Understanding the mechanisms of this bioluminescence process could inform the design of a light stick that works for several days or, with further optimization, environmentally friendly garden and street lighting."
De Meulenaere was scheduled to present this research at the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology annual meeting in San Diego this month. Though the meeting, to be held in conjunction with the 2020 Experimental Biology conference, was canceled in response to the COVID-19 outbreak, the research team's abstract was published in this month's issue of The FASEB Journal.
After discovering that light production was not linked with any of the organism's metabolic pathways, the researchers realized that sustaining light production for more than a few milliseconds would require the slime to contain its own energy source.
Further work revealed that the worm's slime contains an iron storage protein called ferritin. Artificially adding iron to the mucus increased light production, which led the researchers to believe that ferritin acts as like a molecular battery that stores energy. More recently, they found that exposing ferritin to blue light makes more iron available and that exposing the slime to blue light induces bursts of light lasting several minutes.
"A light source based on this mechanism could be remotely triggered using blue light to initiate and amplify the process," said De Meulenaere. "Once we understand exactly how light production happens in the natural system, that information could potentially be used to develop a long-lasting light that is also biodegradable and rechargeable."
The tube worm's bioluminescence could also be used to create biomedical reporter systems. Because it is sensitive to iron such a system could be used to test for iron deficiencies or toxicities. It could also be used as a light-emitting reporter that works for several days. This would allow experiments where various proteins or cells are tracked for much longer periods of time than possible with today's fluorescent reporters.
Journal information: FASEB Journal
Provided by Experimental Biology