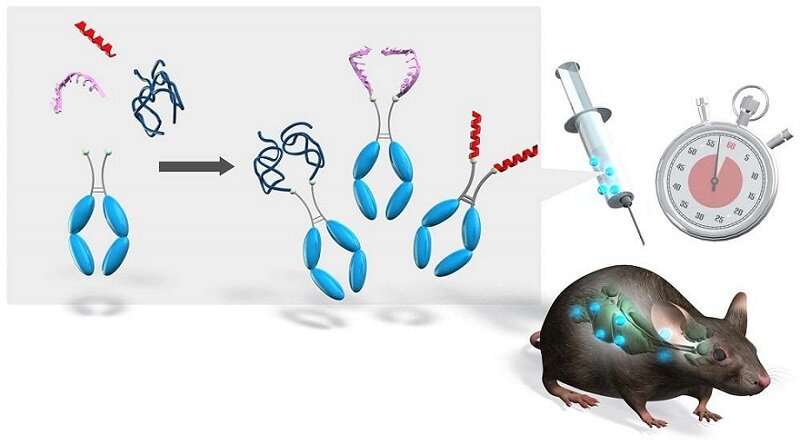
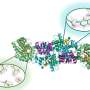
Biopharmaceutic-Fc conjugate synthesized by our method possessed a long half-life inside the body. Credit: University of Electro Communications
Biopharmaceutics consisting of middle molecules, for example, peptide or nucleic-acid aptamers, have been attracting attention as promising molecular modalities in current drug discovery.
A major problem of such pharmaceutics for therapeutic applications is that the half-lives of their circulating plasma inside the body are too short. Ideally, a precise conjugation of the Fc fragment of human antibodies with pharmaceutics would extend the half-lives. Practically, the conjugation between the complicated molecules is still immature.
Now, Masumi Taki and colleagues at the University of Electro-Communications (UEC), and Ajinomoto Co. Inc. have established a facile and efficient semisynthesis method to obtain biopharmaceutics-Fc conjugates.
A combination of chemoenzymatic novel reaction (i.e., the NEXT-A reaction) followed by well-known click reaction yielded almost 100% conversion; and the N-terminal specific precise conjugation of the Fc fragment with different kinds of biopharmaceutics was unambiguously identified by several methods including deconvoluted mass spectrometry.
A Fc-conjugated (peptidic) pharmaceutic synthesized by this method led to a long-circulating plasma half-life inside mice while retaining its original biological activity.
The Fc-conjugation platform described can be applied many kinds of biopharmaceutics with different molecular modalities.
More information: Shigeo Hirasawa et al. Facile and Efficient Chemoenzymatic Semisynthesis of Fc-Fusion Compounds for Half-Life Extension of Pharmaceutical Components, Bioconjugate Chemistry (2019). DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00235
Journal information: Bioconjugate Chemistry
Provided by University of Electro Communications