Fragmentation within intact forests has a higher impact on vertebrate biodiversity than equivalent losses in already degraded landscapes, but the relationship between forest 'intactness' and extinction risk has not been quantified.
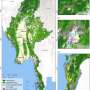
In a new Animal Conservation study, researchers assessed the threat to forest-dependent birds (about 23 percent of all the world's birds) in relation to the proportion of forest within their distributions that remains intact.
The investigators found a remarkably strong positive relationship between global extinction risk of forest birds and the loss of forest intactness within their distributions. Furthermore, most global hotspots of restricted ranges for forest birds now fall in areas of degraded and disturbed (non-intact) forests.
"Our results add weight to recent suggestions that intact forest landscapes have an environmental importance that is disproportional to their area, and indicate that restoring intactness to forests is likely to make a significant contribution to reducing global extinction risk," said lead author Dr. Paul F. Donald, of BirdLife International, in the UK.
More information: P. F. Donald et al, Loss of forest intactness elevates global extinction risk in birds, Animal Conservation (2018). DOI: 10.1111/acv.12469
Provided by Wiley