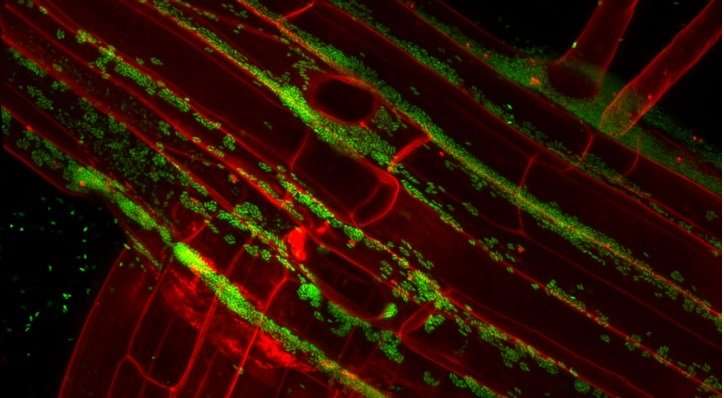
Scanning confocal micrograph of the root surface (red) of the study plant colonized by SA187 (green). Credit: Lukas Synek
Bacteria isolated from desert plants could provide the key to maintaining productive agriculture in arid regions.
As climate change and rising population threaten food security, farmers are under pressure to increase crop yields on marginal lands, such as deserts. Such agriculture requires intensive irrigation, often with highly saline groundwater, and the land can rapidly become salinized to levels inhibiting crop growth.
There is an urgent need to develop crops that can tolerate environmental stresses, including salinity, drought and extreme temperatures. Heribert Hirt's research team at KAUST have found a novel way to do this, exploiting the natural capacity of certain bacteria to stimulate crop growth.
The research team isolated more than 80 different bacteria from inside desert plants and screened them for potential to enhance salt tolerance inArabidopsis—thelab ratof plant science. One species,Enterobacter, known as SA187, clearly outperformed the rest.
Next, the researchers tested SA187 under field conditions using alfalfa, a legume grown in many parts of the world for animal feed. The yield obtained from seed coated with SA187 was significantly higher than that from uncoated seed, under both normal and saline conditions.
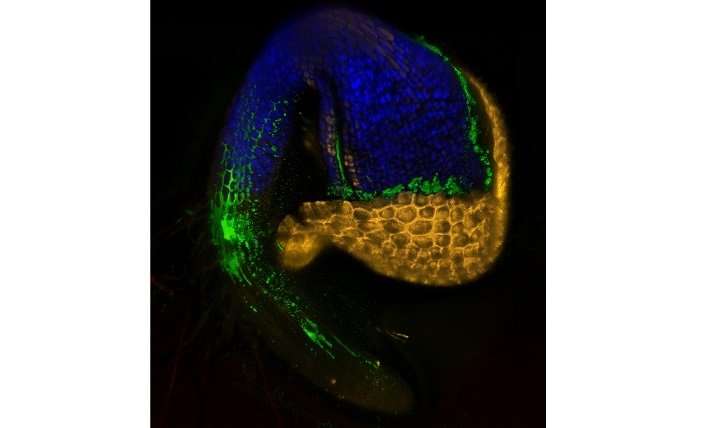
Scanning confocal micrograph of a germinating Arabidopsis seedling, showing immediate colonization by SA187 (green). Credit: Lukas Synek 2017
To understand exactly how SA187 promotes plant growth, the team returned toArabidopsis, where imaging studies showed that SA187 colonizes both roots and shoots. Normally, salt stress limits the rate of photosynthesis, the process by which plants synthesize sugars. In SA187-treated plants, however, photosynthesis continued in highly saline conditions.
Using mutant Arabidopsis, the researchers showed that this effect was mediated by ethylene, a plant hormone thought to be important in adaptation to environmental stresses. However, ethylene was not generated by the plants. Instead, upon colonizing a plant host, SA187 produces large quantities of a compound known as 2-keto-4-methylthiobutyric acid (KMBA). KMBA is easily converted into ethylene in plant cells, and the team showed that this was responsible for improved growth under saline conditions.
The newly discovered KMBA-mediated pathway of molecular communication between bacteria and plants could, the researchers say, be harnessed as "a simple biological solution to growing plants under extremely adverse conditions." Its potential extends beyond alfalfa: postdoc Axel de Zélicourt reports that recent tests in cereals have similar positive outcomes, and trials are underway with tomatoes, cucumbers and melons.
In combination with other bacteria that could, for instance, supply nutrients or stimulate plants' pathogen defenses, de Zélicourt believes this technology could have real benefits for agriculture whilst reducing its environmental impact. Our ultimate aim, he says, "would be to offer farmers and breeders a bacterialcocktailto boost crop yields in adverse environments."
More information: Axel de Zélicourt et al. Ethylene induced plant stress tolerance by Enterobacter sp. SA187 is mediated by 2‐keto‐4‐methylthiobutyric acid production, PLOS Genetics (2018). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007273
Journal information: PLoS Genetics