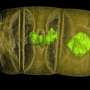
Blue-green algae are one of the oldest organisms in the world and have an important role to play in many ecosystems on Earth. However, it has always been difficult to identify fossils as blue-green algae without any trace of doubt. The reason is their sheath of calcium carbonate. A Master's student at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) has now developed a method to assign organisms to a particular species.
Extinct species often leave very sparse information about their life and biology. Researchers often find puzzling fossils they cannot allocate to any known group, especially dating from the period when many groups of organisms first evolved. Such microscopic organisms are often classed as blue-green algae, as on the surface they resemble the microscopic calcium carbonate sheaths of the algae. Blue-green algae are among the oldest organisms on Earth and play a fundamental role in many marine and terrestrial ecosystems, for example by performing intensive photosynthesis or as food for a number of animals. In spite of their significance, little is known about their evolution, as their fossils are virtually shapeless tubes or bubbles of carbonate. It has therefore proved very difficult for researchers to determine whether fossils belong to blue-green algae or a completely different group of organisms.
Working together with a team of researchers from FAU, Jan-Filip Päßler, a master's student in palaeobiology at FAU, has examined the crystallography of fossil structures using methods derived from materials science. Päßler compared carbonate fossils, so-called trilobites, with two microfossils which had not yet been able to be assigned, but which were extremely common in the oceans approximately 400 million years ago. He based his comparison on the observation that biologically formed carbonate structures have a very specific pattern. What is more, organisms form their skeletons in different ways—and these differences become apparent in the way crystals are arranged in the carbonate. Researchers were not only able to measure the direction in which crystals grew, but also misorientations between adjacent crystals. They found that in blue-green algae the crystals follow a less structured pattern with many misorientations. Trilobites, however, have an ordered structure with fewer misorientations. According to Päßler's supervisor, Dr. Emilia Jarochowska, 'our approach can be used in future to clarify the biological relationships between many other mysterious fossils in geological history'.
More information: Jan-Filip Päßler et al, Distinguishing Biologically Controlled Calcareous Biomineralization in Fossil Organisms Using Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD), Frontiers in Earth Science (2018). DOI: 10.3389/feart.2018.00016
Provided by University of Erlangen-Nuremberg