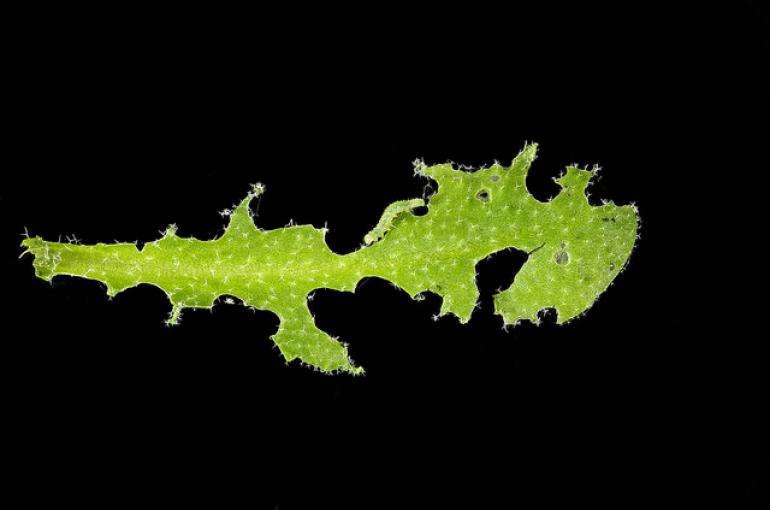
Arabidopsis with caterpillar. Credit: Hans van Pelt, Utrecht University
The hormone jasmonic acid plays a major role in the plant immune system and in regulating growth. Scientists have already learned much about how jasmonic acid works, but one important link was missing: what makes the plant's jasmonic acid level go down once the attack by a fungus or insect has been warded off? Plant biologists at Utrecht University and colleagues from the University of Amsterdam, have now discovered how the plant metabolises jasmonic acid, issuing the signal 'safe'. Controlling this mechanism may present new opportunities to increase resistance of crops to fungi and insects. The results of their research were published in the scientific journal PNAS on Tuesday 30 May.
Once a plant detects an insect or fungus, it begins to produce the hormone jasmonic acid, which initiates an immune response that prevents further damage. After the attack, jasmonic acid is quickly broken down again. This is necessary because the hormone inhibits plant growth and development.
Four enzymes
Until now, scientists did not know how jasmonic acid is broken down in the plant. But in their research on the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, biologists at Utrecht University and the University of Amsterdam have discovered that four related enzymes have this activity.
Missing link
Each of these four enzymes can perform a chemical reaction in which an oxygen atom is added to jasmonic acid. This creates an inactive variant of the hormone, 12-hydroxy-jasmonic acid. While high concentrations of jasmonic acid activate the plant's immune system, this does not occur with the inactive variant. With this discovery, the scientists have found an important missing link as to how the plant controls its levels of jasmonic acid.
Left a ‘normal’ plant with a fungal infection, right a plant in which the enzymes have been switched off. By switching off the enzymes, the plant on the right has increased resistance to the fungus, and therefore displays less disease symptoms. But it clearly also has consequences for the plant’s growth and development. Credit: Utrecht University
Increasing resistance
"Now that we know about these enzymes, we have the opportunity to control the concentration of jasmonic acid in order to increase the plant's resistance", explains research leader Prof. Guido Van den Ackerveken from Utrecht University. "Our research shows that plants are much more resistant to insects and pathogenic fungi if we turn off the four enzymes in a plant. One major disadvantage to this, however, is that it inhibits the plant's growth and development. So the trick is to find the right balance.".
More information: 'Arabidopsis JASMONATE-INDUCED OXYGENASES down-regulate plant immunity by hydroxylation and inactivation of the hormone jasmonic acid' PNAS, 30 May 2017
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by Utrecht University