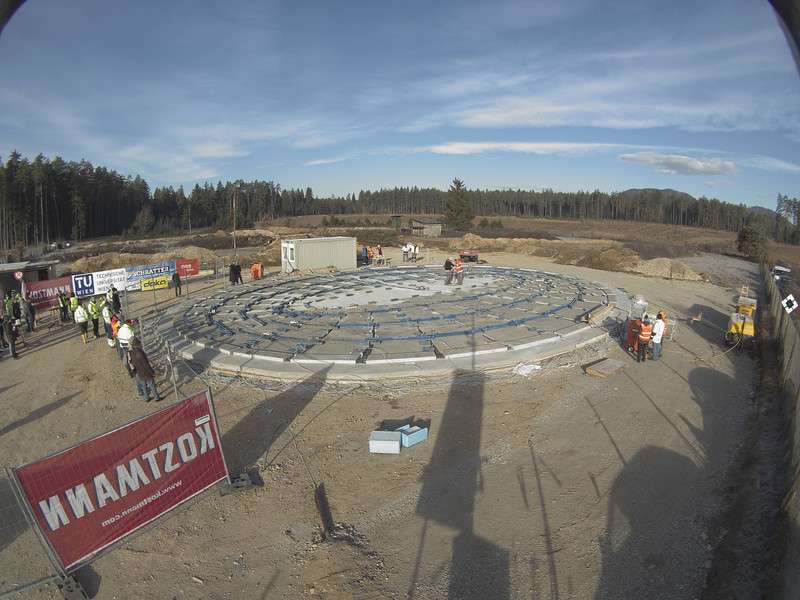
Initially flat slab before inflation. Credit: Vienna University of Technology
At TU Wien, an alternative for resource intensive formwork for the construction of concrete domes was developed. It is now used in a test dome for the Austrian Federal Railways Infrastructure.
Concrete shells are efficient structures, but not very resource efficient. The formwork for the construction of concrete domes alone requires a high amount of labor and material. A very resource efficient alternative construction method called "Pneumatic Forming of Hardened Concrete (PFHC)" was invented at TU Wien by Dr. Benjamin Kromoser and Prof. Johann Kollegger at the Institute of Structural Engineering. A simple air cushion and additional post-tensioning tendons transform a flat concrete plate into a double curved shell. Thus, the complicated spatially curved formwork and the framework are redundant. The Austrian Federal Railways Infrastructure (ÖBB Infrastruktur) are currently building a first test construction on a scale of 1:2 in Carinthia, in the south of Austria, which will later serve as event canopy.
The "Pneumatic forming of hardened concrete" construction method
The functioning of the construction method is comparatively easy: At first a flat concrete plate with wedge-shaped outlets is casted. After the concrete is hardened, the air cushion placed underneath the plate is inflated and the post-tensioning tendons at the circumference are tensioned until the final form is reached. Glass fiber reinforced plastic rods used as reinforcement absorb the occurring strains in the concrete plate. If the flat plate is produced with high accuracy, the construction method allows to build very precise concrete shells. The method also saves up to 50 percent of the concrete as well as 65 percent of the necessary reinforcement steel.
Credit: Vienna University of Technology
ÖBB test dome as event canopy
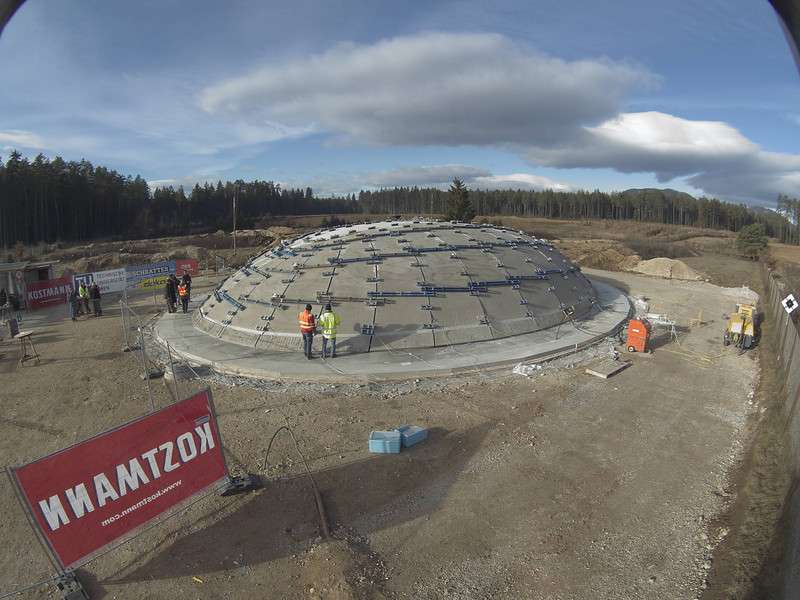
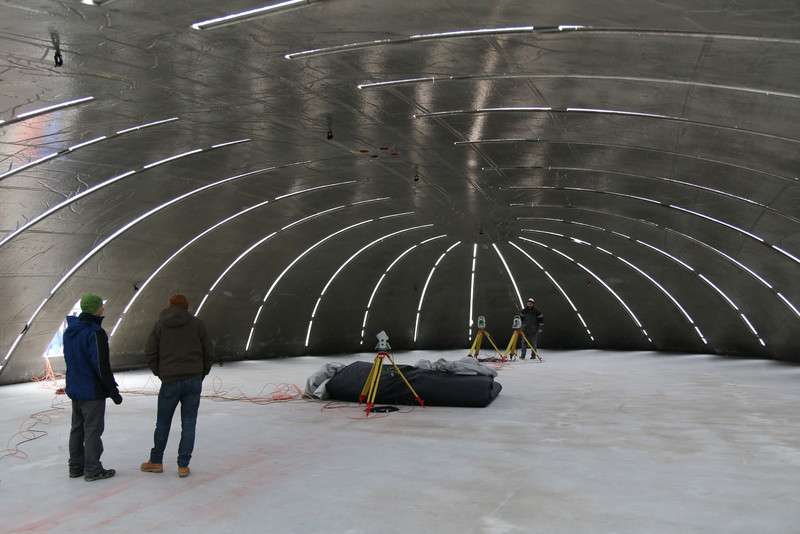
The test dome, built on behalf of the ÖBB Infrastruktur, has a length of 26.5 m, a width of 19.1 m and a height of 4.2 m. It will be used it to improve the construction technique for a first large application on a deer pass over the twin-track railway line "Koralmbahn" in 2017. Recently, the transformation process of the test dome was successfully finished, weighing 80 t and lifted with only 20-22 millibar from the flat plate to the spatially curved shell. The very smooth surface results from a sophisticated geometry optimization. "We could improve the construction method once again decisively during the preparation of the project for this first application", explains Dr. Benjamin Kromoser. In the next work steps, an additional concrete layer will be applied and some areas will be cut away. The final building can already be used for events in summer 2017.
-
Finished concrete shell after the transformation process. Credit: Vienna University of Technology
-
Prepared concrete shell for the application of an additional concrete layer. Credit: Vienna University of Technology
-
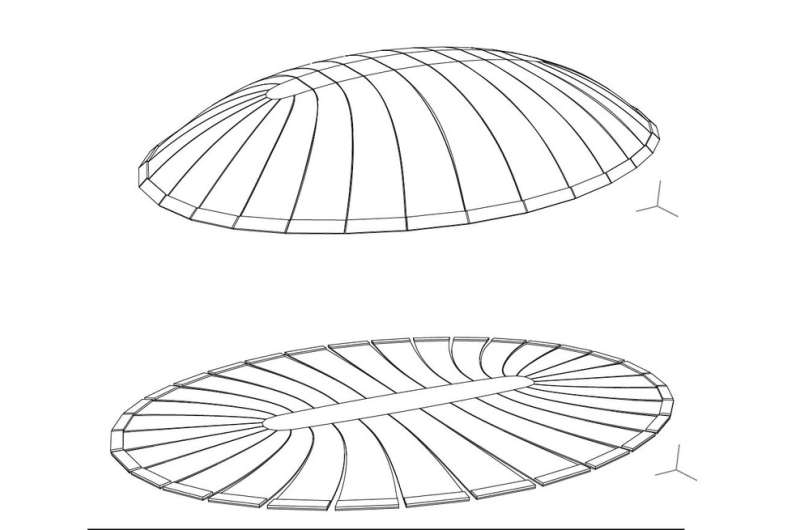
Geometry optimized dome and unrolled initially flat slab before inflation. Credit: Geometry optimization DI Thomas Pachner
-
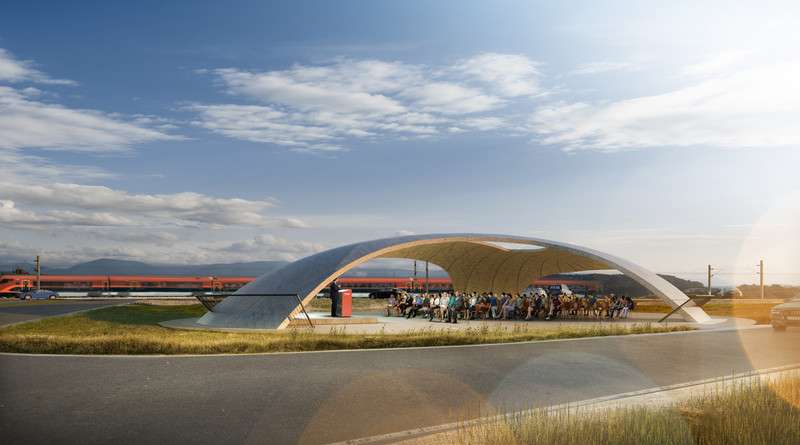
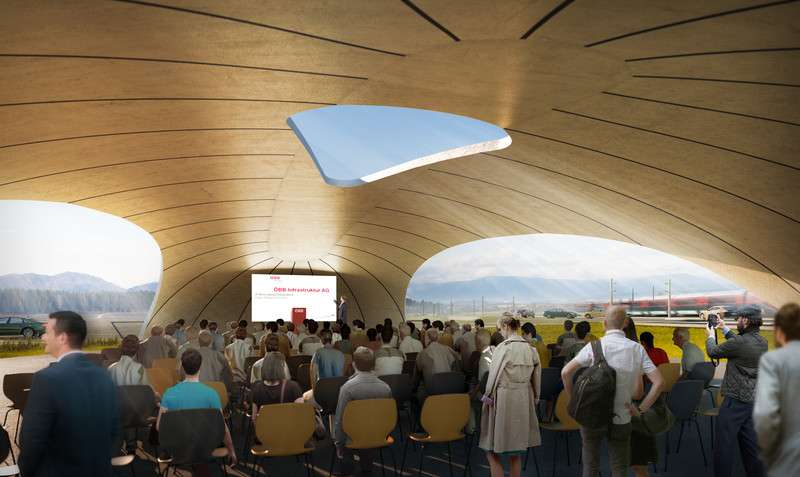
Visualization of the finished event canopy with view from outside. Credit: Martin Ritt, MA; Rendering DI Michael Sohm
-
Visualization of the finished event canopy. Credit: Martin Ritt, MA; Rendering DI Michael Sohm
-
Surveying work inside the concrete shell. Credit: Vienna University of Technology
Provided by Vienna University of Technology