Credit: Lund University
Many biological processes in cells function solely due to the phenomenon of diffusion. This ensures that particles are able to move randomly and aimlessly on the basis of their thermal energy alone. In this way, protein molecules get into close enough proximity to each other to, for example, carry out metabolic processes only achievable when acting together.
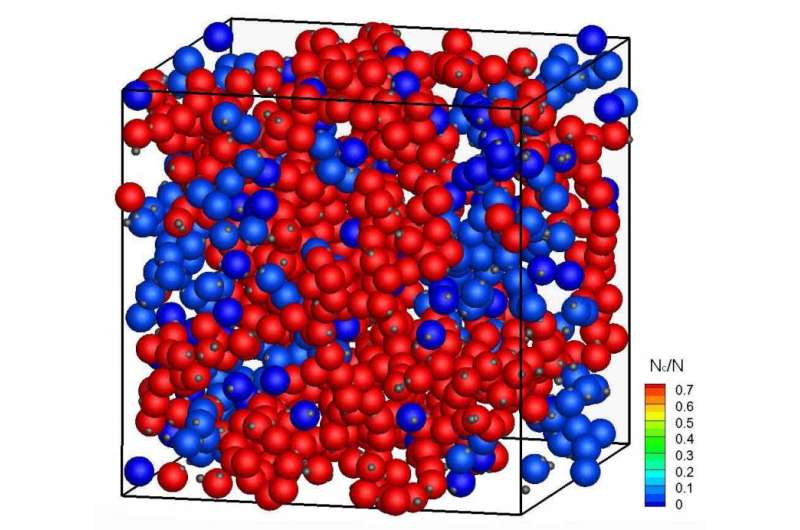
A team of international researchers has now shown that weak attraction forces between proteins can enormously influence diffusion, if the protein molecules are as densely concentrated as under natural conditions in living cells.
The influence of interactions in such high protein concentrations is extremely difficult to quantify experimentally. Because of this, until now many measurements have been made in diluted solutions.
Neutron scattering experiments performed among other places at the Jülich outstation at the Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Zentrum in Garching, and computer simulations carried out in Jülich have now made studies possible in physiological concentrations.
The results verify on one hand the excellent suitability of neutron scattering for this type of experimental work and on the other, that computer simulations must take the specific molecular properties of proteins, such as their surface structure, far more into consideration in order to arrive at realistic predictions.
More information: S. Bucciarelli et al. Dramatic influence of patchy attractions on short-time protein diffusion under crowded conditions, Science Advances (2016). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1601432
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres