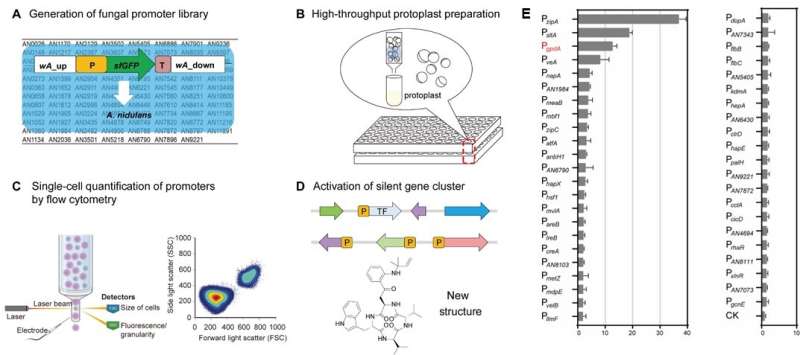
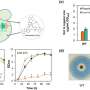
(A) Fungal promoter library was generated on the basis of the selected promoter sequences from the Aspergillus Genome Database. (B) Protoplasts were prepared in a 24-well microtiter plate and collected for high-throughput flow cytometry (FC) detection in a 96-well microtiter plate. (C) FC-based single-cell quantitative method was established for the detection of gene expression in A. nidulans. (D) The screened promoters were applied for silent biosynthetic gene activation and novel structure discovery. (E) Relative strengths of 43 fungal promoters with >1.5-fold expression level over the commonly used PgpdA. Credit: Science China Press
Natural products (NPs) are low-molecular-weight compounds derived from secondary metabolic pathways, which are regulated by hierarchical regulatory networks from cluster-specific regulators to global transcriptional complexes.
A study recently published in Science China Life Sciences aimed to identify new promoters that can be used in synthetic biology to activate silent BGCs. However, characterization of filamentous fungal regulatory elements remains challenging because of time-consuming transformation technologies and limited quantitative methods.
The research team established a method for quantitative assessment of filamentous fungal promoters based on FC detection of the superfolder green fluorescent protein at single-cell resolution. Using this quantitative method, they acquired a library of 93 native promoter elements from Aspergillus nidulans in a high-throughput format.
The strengths of identified promoters covered a 37-fold range by flow cytometry. PzipA and PsltA were identified as the strongest promoters, which were 2.9- and 1.5-fold higher than that of the commonly used constitutive promoter PgpdA.
To validate the reliability and accuracy of the FC-based quantitative method, promoters showing gradient strength levels were selected for assessment by mRNA levels as analyzed through quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), confocal laser-scanning fluorescence microscopy, and yield comparison of the activated neosartoricins. Indeed, the corroborative results validated the reliability of their method to identify promoter activities.
Furthermore, the research team applied the selected strong promoters PzipA and PsltA to activate a silent nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene Afpes1 from the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus.
The metabolic products of Afpes1 were identified as new cyclic tetrapeptide derivatives, namely, fumiganins A and B. This study provides a highly efficient strategy for the quantitative characterization of promoters of filamentous fungi. The application of regulatory elements will promote the discovery and synthetic biological creation of novel fungal NPs.
More information: Peng-Lin Wei et al, Quantitative characterization of filamentous fungal promoters on a single-cell resolution to discover cryptic natural products, Science China Life Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11427-022-2175-0
Journal information: Science China Life Sciences
Provided by Science China Press