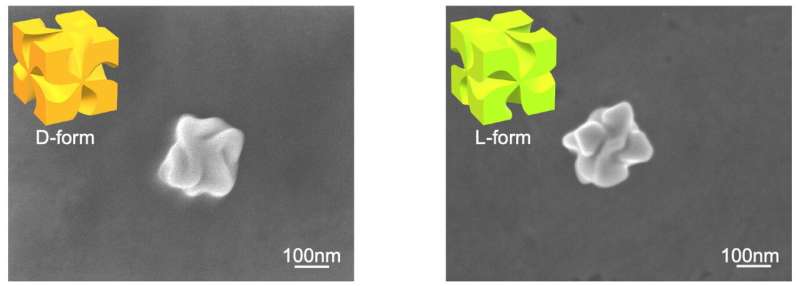
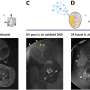
Scanning electron microscopy images show D- and L- form gold chiral nanoparticles. The insets visualize the three-dimensional models of the nanoparticles. Credit: NINS/IMS
Researchers investigated the polarization-dependence of the force exerted by circularly polarized light (CPL) by performing optical trapping of chiral nanoparticles. They found that left- and right-handed CPL exerted different strengths of the optical gradient force on the nanoparticles, and the D- and L-form particles are subject to different gradient force by CPL. The present results suggest that separation of materials according to their handedness of chirality can be realized by the optical force.
Chirality is the property that the structure is not superimposable on its mirrored image. Chiral materials exhibit the characteristic feature that they respond differently to left- and right-circularly polarized light. When matter is irradiated with strong laser light, optical force is exerted on it. It has been expected theoretically that the optical force exerted on chiral materials by left- and right-circularly polarized light would also be different.
The research group at Institute for Molecular Science and three other universities used an experimental technique of optical trapping to observe the circular-polarization dependent optical gradient force exerted on chiral gold nanoparticles. Chiral gold nanoparticles have either D-form (right-handed) or L-form (left-handed) structure, and the experiment was performed using both.
The optical force exerting on the nanoparticle is dependent on the handedness of the circularly polarized incident light. Credit: NINS/IMS
Although the optical gradient force acting on chiral nanoparticles was predicted theoretically, no observation of the force has been reported before. The research group succeeded in observing the optical gradient force originating from the chirality (i.e., the difference between the gradient force by left- and right-circularly polarized light), by optical trapping of the chiral gold nanoparticles.
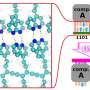
Chiral materials exhibit the characteristic feature that they respond differently to left- and right-circularly polarized light (optical activity). The response of D-form molecule to left-circularly polarized light is same as that of L-form molecule to right-circularly polarized light, and vice versa. Credit: NINS/IMS
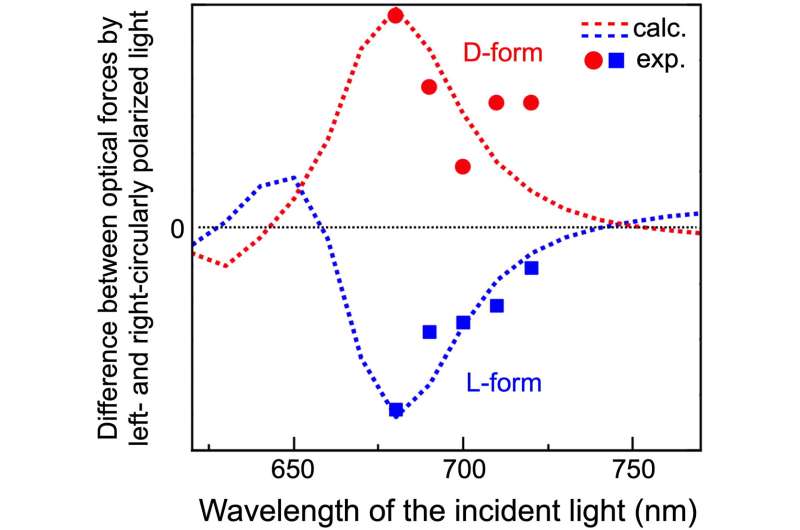
The results showed that the optical gradient force was different for D-form and L-form particles. The researchers also found, from the dependence of the force on the wavelength of the light used, that there is a previously unknown effect on the mechanism of the chirality-dependent optical forces.
The plots are the experimental data and broken line are the theoretical calculation. Red and blue in the plots and line represents the D- and L-form nanoparticles, respectively. The optical gradient force was different for D-form and L-form particles. Credit: NINS/IMS
The present study clarified the characteristics of the circular-polarization dependent optical gradient force on the mechanics of chiral gold nanoparticles. It shows the possibility of separation of chiral materials by the optical force, which may be realized by using locally confined light generated on nanostructures to trap the materials and/or by utilizing the optical force of other mechanisms.
The research was published in Science Advances.
More information: Junsuke Yamanishi et al, Optical Gradient Force on Chiral Particles, Science Advances (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq2604. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abq2604
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by National Institutes of Natural Sciences