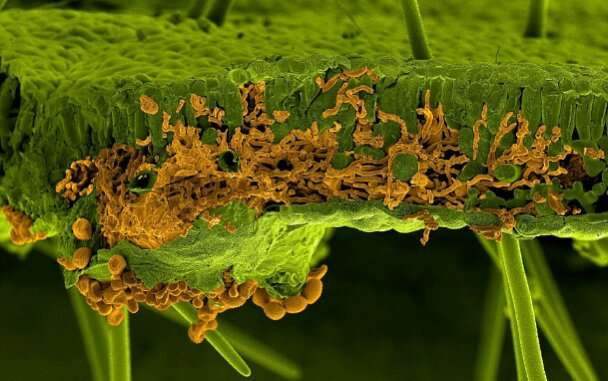
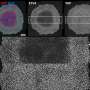
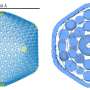
Scanning electron microscopy picture of a soybean leaf infected by the rust fungus Phakopsora pachyrhizi. The leaf and the fungus were artificially painted in green and in orange, respectively. The section shows invading infection hyphae of the fungus inside the leaf mesophyll, whereas the spores are visible below the leaf breaking through the lower epidermis. Credit: U. Steffens, Bayer Crop Science
The United States is the world's leading soybean producer, and soybeans are used to produce biodiesel. The fungus Phakopsora pachyrhizi causes Asian Soybean Rust (ASR) and is the major pathogen of soybean. Left uncontrolled, soybean rust could reduce crop yields by as much as 90 percent.
As part of the DOE Joint Genome Institute's 2016 Community Science Program portfolio, Sebastien Duplessis of the French National Institute for Agricultural Research (INRA) proposed sequencing a reference genome for P. pachyrhizi to develop better strategies to counter soybean rust disease. Soybean itself is a JGI Flagship plant genome, and JGI published its genome sequence in 2010.
On September 30, all available data from an international consortium's efforts to sequence three P. pachyrhizi isolates, including the one done by the JGI, are accessible on the JGI's fungal portal MycoCosm at https://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov/Phapa1.
Provided by DOE/Joint Genome Institute