Opportunity’s final image before the global dust storm ended the rover’s mission on Mars. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell/ASU
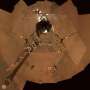
Opportunity's final message home is not much to look at on its own. If you're old enough to remember film cameras, it looks like the final exposure on a roll of film, developed but partly missing. It's a suitable epitaph for Opportunity's mission.
Opportunity captured this image with the left half of its PanCam, or Panoramic Camera. The rover had the solar filter on the camera at the time, which is why the image is so dark. The bottom is cut off because it was unable to transmit the entire image before losing power.
It bears similarity to Opportunity's first image from Mars, also taken with the left Panoramic Camera.
The image was captured on the 5,111th Martian Sol, in the Perseverance Valley. It was captured at about 9:30 a.m. PDT (12:30 p.m. EDT) on June 10, 2018, one year ago today. It transmitted the image up to the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter at about 9:45, then on to Earth. It arrived here at about 10:05 a.m. PDT (1:05 p.m. EDT), where it was received by one of the stations in NASA's Deep Space Network.
The image is dark because the sun was blanked out by the global dust storm that enveloped Mars at the time. The graininess is camera noise. The black area at the bottom represents the data that was never received. Opportunity died before it could send the rest.
Two thumbnails from Opportunity’s final images. The Sun is a tiny dot. They were taken to estimate the opacity of the atmosphere during the global dust storm. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell/ASU
It's actually not the final image from Opportunity, but it is the final full-frame image. The rover sent thumbnails from other images, but none of the full images were sent before Opportunity went down.
Over the course of its mission on Mars, Opportunity took over 228,000 images. You can see all 228,771 raw images here. That's an un-curated collection, though.
Opportunity’s final panorama image from the surface of Mars is of Endeavour Crater. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell/ASU
Provided by Universe Today