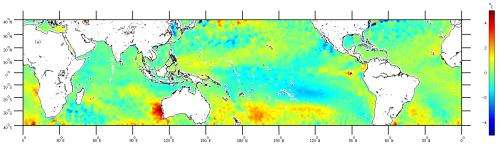
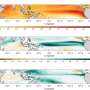
Sea surface temperature anomalies during 21 February – 6 March 2011 at the peak of the extreme warming event.
(Phys.org)—Abnormal climatic conditions in the Indian and Pacific Oceans during the 2010-2011 La Niña event combined to create the extreme marine heatwave seen off the Western Australia coast in 2011, according to a new paper published in Nature Scientific Reports.
Lead author Dr Ming Feng, from CSIRO's Wealth from Oceans Flagship, says the marine heatwave was driven by unusual features in the Leeuwin Current - a warm ocean current which flows southwards near the west coast of Australia – which was affected by extreme ocean and atmospheric conditions in the Pacific and Indian Ocean during the 2010-2011 La Niña.
"Record easterly wind in the eastern Pacific and record northerly wind in the southeast Indian Ocean combined to produce an unseasonable surge of the southward-flowing Leeuwin Current and extreme ocean warming off the west coast of Australia," Dr Feng said.
Water temperatures were recorded by satellite, robotic Argo profilers and continental shelf moorings operated as part of Australia's Integrated Marine Observing System. During the heatwave water temperatures were more than 3ºC above long-term seasonal averages, climbing up to 5ºC above for a two-week period at the peak of the event, and causing widespread impacts on marine ecology, including fish kills and coral bleaching.
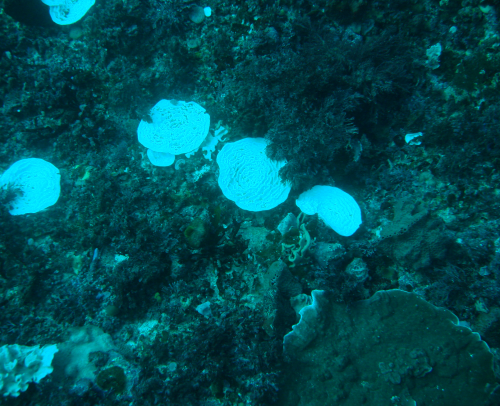
Coral bleaching in water off Rottnest Island taken in May 2011.
Water temperatures affect the growth, survival, abundance and distribution of most marine species. Rapid short-term temperature rises can be harmful or even lethal to marine organisms, as in the case with coral bleaching and fish mortality, and have potentially catastrophic impacts on marine ecosystems throughout the world's oceans.
The seasonal sea surface temperature warming off the west coast of Australia has been termed a 'Ningaloo Niño', an analogy to other eastern continental boundary current warming phenomena such as El Niño in the Pacific and the Benguela Niño in the Atlantic.
"Understanding the factors that influence the formation of events like the 2011 Ningaloo Niño is a vital first step in preparing for impacts from extreme warming events in the future," said Dr. Feng.
Co-author, Dr Michael McPhaden of the Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory, NOAA, said the research demonstrated the significance of far-away events to our own backyard.
"Nature always finds a way to surprise us and the Ningaloo Niño is just the latest episode in this continuing saga.
"This is research that matters to society because it tells us that what happens in your backyard can be influenced by events happening in far away places and at times in the distant past," Dr McPhaden said.
More information: Feng, M., et al. La Niña forces unprecedented Leeuwin Current warming in 2011. Scientific Reports 3, 1277; DOI:10.1038/srep01277 (2013).
Background information on the ecological impact of the 2011 marine heatwave can be found in a report prepared for the Western Australia fisheries department.
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by CSIRO