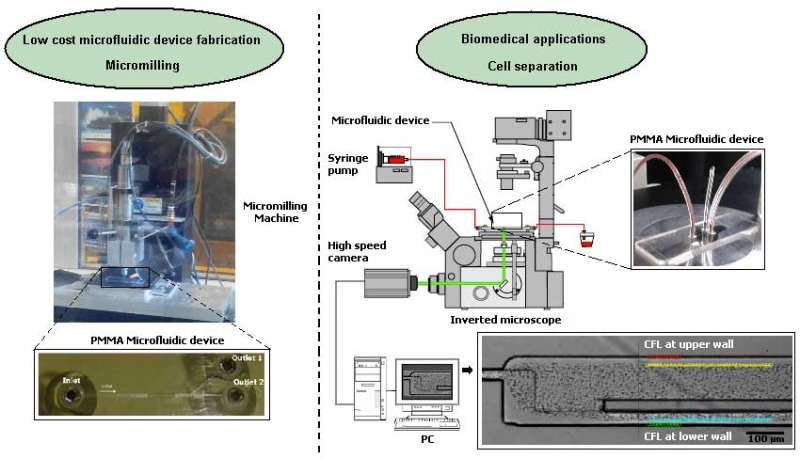
Recently, researchers were able to produce milling tools smaller than 100 m and consequently have promoted the ability of the micromilling machines to fabricate microfluidic devices capable of performing cell separation. Credit: Dr. Diana Pinho, Bentham Science Publishers
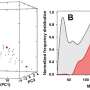
The researchers show the ability of a micromilling machine to manufacture microchannels down to 30 µm and also the ability of a microfluidic device to perform partial separation of red blood cells from plasma.
In this work, Dr. Diana and fellow researchers propose a low cost technique able to produce microfluidic devices for biomedical applications. The most common technique to fabricate biomedical microdevices is soft-lithography. However, it is a costly and time-consuming technique. Progress in manufacturing milling tools smaller than 100 µm, has enabled the use of micromilling machines to fabricate microfluidic devices capable of performing cell separation.
The researchers show not only the ability of a micromilling machine to fabricate microchannels down to 30 µm but also the ability of the manufactured microfluidic device to perform partial separation of red blood cells from plasma. They have performed blood flow visualization and measurements of the cell-free layer thickness by using a high-speed video microscopy system and demonstrated the advantages and limitations of the described micromilling fabrication technique to produce microfluidic devices for cellular-scale flow studies.
More information: Jaron Singhal et al. Blood Flow Visualization and Measurements in Microfluidic Devices Fabricated by a Micromilling Technique, Micro and Nanosystems (2016). DOI: 10.2174/1876402908666160106000332
Provided by Bentham Science Publishers