Intense and rare rainfall in California's famous Death Valley caused major flooding.
Hours after rare and intense flooding hit California's Death Valley, closing roads and stranding some 1,000 people, waters were receding Saturday and police escorted many of those trapped to safety.
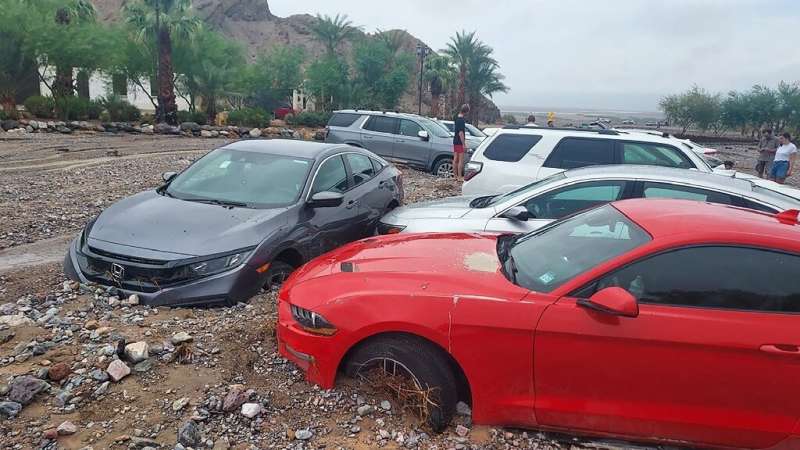
After "unprecedented amounts of rainfall caused substantial flooding" in the famously parched park, around 60 cars were bogged down under mounds of debris, the National Park Service (NPS) said.
"Aerial searches are underway to ensure that there are no stranded vehicles in remote areas," the Death Valley National Park said on its website Saturday.
"Hard work from road crews allowed visitors who were previously unable to leave the area hotels to be able to carefully drive out with law enforcement escorts," the park said.
"At this time, there are no reported stranded visitors on park roadways and no reported injuries."
Earlier, the NPS said that about 500 visitors and 500 staff had been "unable to exit the park," which is in the Mojave Desert, straddling the California-Nevada border.
Death Valley, with its vast sand dunes, scorching salt flats and endless badlands, is the largest national park in the 48 lower states.
It is the hottest and, normally, the driest of the national parks.
But the recent floodwaters tore up sections of paved roads, pushed dumpster containers into parked cars, and flooded offices and hotels.
"With over 1,000 miles of roadway in the park, and 3.4 million acres," the NPS said, "it will take time to get a full assessment of the damage."
The park service said that all roads serving the park will remain off-limits for now.
Park Superintendent Mike Reynolds added that "with the severity and widespread nature of this rainfall it will take time to rebuild and reopen everything."
A total of 1.46 inches (3.7 centimeters) of rain fell in the park's Furnace Creek area, almost tying the previous daily record of 1.47 inches. The average annual rainfall is less than two inches a year.
According to UN climate experts, even if the world manages to limit warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius, some regions will experience increasingly intense and frequent rainfall.
© 2022 AFP