Credit: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/ J. R. Goicoechea (Instituto de Física Fundamental, CSIC, Spain)
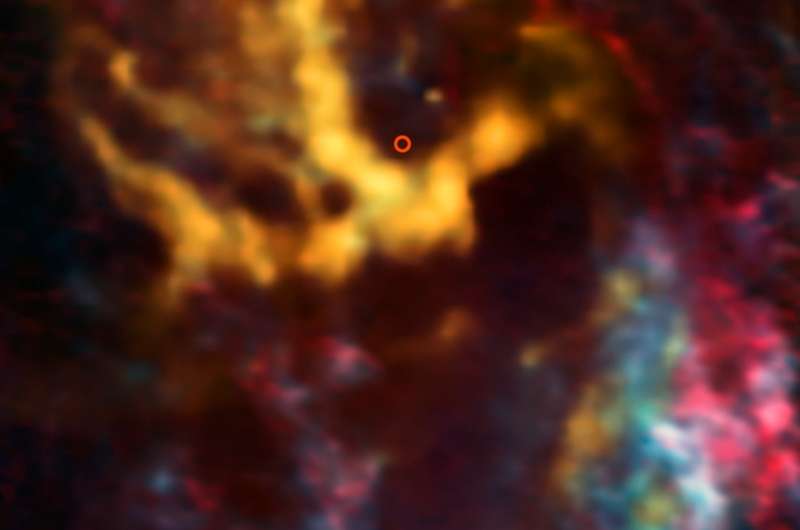
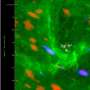
This image from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) shows the area surrounding Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole that lurks at the centre of the Milky Way—highlighted here with a small circle. New research has revealed exciting evidence of interstellar gas and dust orbiting the black hole at high speeds.
The molecular-hydrogen-rich gas clouds which have been identified are known as molecular cloudlets, and they have never before been unambiguously detected. This image actually shows the distribution of molecules including carbon monoxide, the cloudlets' second most abundant molecular component. The cloudlets lie 26 000 light-years away from us, orbiting fast and relatively close to the black hole, at a distance of about one light year. ALMA's high resolution allowed scientists to detect the cloudlets, which are the products of pre-existing massive clouds rotating around the centre of our galaxy. These clouds were tidally disrupted into dense fragments and a lower density, short-lived component. The latter was identified thanks to the signs left by the passage of the synchrotron radiation emitted by Sagittarius A* through diffuse gas between the cloudlets.
Although clouds of molecular gas have the potential to form new stars, these cloudlets are unlikely to create stellar newborns. They have a comparatively small mass of around 60 times that of the Sun, and exist close to the huge, turbulent, punishing gravitational forces exerted by Sagittarius A*.
While the stars orbiting Sagittarius A* have been systematically observed, these dense molecular cloudlets have not been detected so close to the centre of our galaxy before.
Provided by ESO