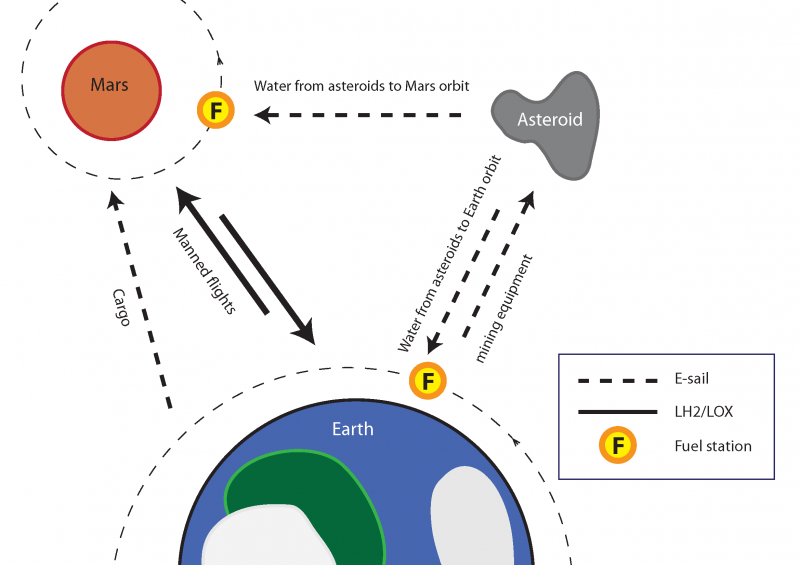
The E-sail is a novel propellantless technology that was invented in Finland in 2006. The E-sail utilises long, charged tethers to convert natural solar wind momentum flux into spacecraft thrust.
According to Janhunen et al. (2015) the E-sail could make asteroid mining feasible by providing essentially free logistics in the solar system outside of Earth's magnetosphere. After finding a suitable water bearing asteroid, a mining unit is could be sent by the E-sail to extract the water from asteroid soil. This can be done by heating the material and letting the evolving water vapour condense in a cool container. When the container is full, it is separated from the mining unit and transported with an E-sail in to the orbit of Mars or Earth, where it is split into hydrogen and oxygen and liquefied. The liquid hydrogen/oxygen (LH2/LOX) fuel can be used to fill the tanks of manned vehicles travelling between Earth and Mars.
Due to the exponential nature of the rocket equation, intermediate tankings reduce the launch mass dramatically. During the trip, asteroid-mined water could also be used as radiation shielding of the manned module to reduce the launch mass further. With cheap propellant available in Mars orbit, there is also the option of fully propulsive landing on Mars which eliminates the need of a massive and expensive heat shield.
The Electric solar wind sail facilitated Manned Mars Initiative, EMMI, could provide a fundamentally new, economically sustainable way to approach manned Mars flights. The running costs of the EMMI are not expected to much exceed those of maintaining the International Space Station.
More information: "EMMI—Electric solar wind sail facilitated Manned Mars Initiative," Acta Astronautica, 113, 22-28, 2015, ISSN 0094-5765, dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.03.029
Provided by Finnish Meteorological Institute