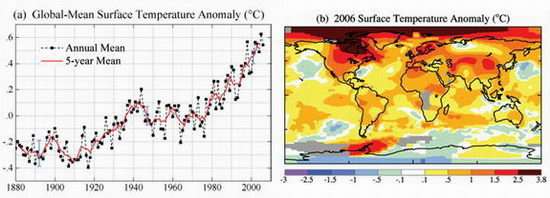
The first graph shows global annual surface temperatures relative to 1951 to 1980 mean, based on surface air measurements at meteorological stations and ship and satellite measurements for sea surface temperature. Over the past 30 years the Earth has warmed by about 0.6°C or 1.08°F. The second image is a color map of temperature anomalies in 2006 relative to the 1951 to 1980 mean. Areas that were warmest in 2006 are in red, and areas that have cooled are in blue. Note that the Arctic has warmed significantly. These temperatures are for the calendar year 2006. Credit: NASA
Climatologists at the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York City have found that 2006 was the fifth warmest year in the past century.
Other groups that study climate change also rank these years as among the warmest, though the exact rankings vary depending upon details of the analyses. Results differ especially in regions of sparse measurements, where scientists use alternative methods of estimating temperature change.
Goddard Institute researchers used temperature data from weather stations on land, satellite measurements of sea surface temperature since 1982 and data from ships for earlier years.
“2007 is likely to be warmer than 2006,” said James Hansen, director of NASA GISS, “and it may turn out to be the warmest year in the period of instrumental measurements. Increased warmth is likely this year because an El Nino is underway in the tropical Pacific Ocean and because of continuing increases in human-made greenhouse gases.”
Most places on the globe have warmed in recent decades, with the greatest warming at high latitudes in the Arctic Ocean, Alaska, Siberia and the Antarctic Peninsula. Most ocean areas have warmed. Climatologists say that warming is not due to local effects of heat pollution in urban areas, a point demonstrated by warming in remote areas far from major cities.
In their analysis for the 2005 calendar year, GISS climatologists noted the highest global annual average surface temperature in more than a century.
Source: by Leslie McCarthy, Goddard Institute for Space Studies