The Air Force Research Laboratory is laying the groundwork to develop revolutionary hypersonic aerospace vehicles. AFRL is examining the feasibility of replacing traditional mechanical actuators, which move to control an air vehicle's flight control surfaces like wing flaps, with plasma actuators that require no moving parts and are more reliable.
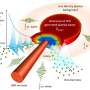
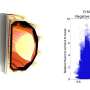
As part of the Air Force Office of Scientific Research Boundary Layers and Hypersonics program, AFRL conducted a wind tunnel test to evaluate the feasibility of using plasma actuators for airframe flight control. In AFRL's Mach 5 plasma channel wind tunnel, engineers used a strong electric field to ionize air around an air vehicle model to create plasma.
Air diverted by plasma heating successfully exerted force on the model and demonstrated that the plasma actuator concept is a viable area for further study and development.
AFRL's Mach 5 plasma channel wind tunnel relies upon a vacuum system to generate low-density air flows. A high electrical voltage placed between metal electrodes on a model in the plasma channel ionizes the air between them and creates plasma, a state of matter where electrons are stripped from molecules. While usually occurring at extreme temperatures and pressures such as the conditions experienced within a star or by a hypersonic vehicle during flight, man-made plasma is found in items like fluorescent light bulbs and computer screen plasma displays.
The Boundary Layers and Hypersonics program is developing knowledge of fluid physics to facilitate future aerospace vehicle designs. The program focuses on characterizing, predicting and controlling high-speed fluid dynamic phenomena including boundary layer transition, shock/boundary layer, shock/shock interactions and other airframe propulsion integration phenomena including real-gas effects, plasma aerodynamics, magnetohydrodynamics and high-speed flow heat transfer.
Copyright 2006 by Space Daily, Distributed United Press International