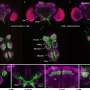
Qtwigs and leaves of Cipadessa baccifera. Credit: CAO Donghua
Cipadessa baccifera is a bushy shrub with pinnate leaves mainly distributed in tropical Asia. It has been traditionally used as folk medicine by Dai people in Xishuangbanna, southwest China for treatment of various diseases such as dysentery, malaria, pruritus (itchy skin), rheum, rheumatism, and burns and scalds.
Previous phytochemical researches on Cipadessa species have led to the isolation of structurally diverse limonoids (e.g., mexicanolides, methyl angolensates, trijugins, and cipadesins).
In the continuing search for biologically active limonoids from Meliaceae plants, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) isolated twelve previously undescribed limonoids and seven known analogs from the leaves and twigs of C. baccifera.
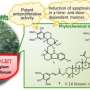
The researchers conducted a phytochemical study on the petroleum ether fraction of the twigs and leaves of C. baccifera. They isolated nineteen mexicanolide-type limonoids including twelve previously undescribed limonoids (1–12) and seven known analogs (13–19).
Moreover, cipaferen R (12) is the first biodegraded tetranortriterpenoid derivative featuring a unique acetyl group at C-17. Among these isolates, no compounds exhibited nematicidal activities against the root knot nematode, M.incognita and antifungal activities against F.oxysporum f. sp. cubense and R.solanacearum.
They also demonstrated that several mexicanolide-type limonoids (1, 14, 17, and 18) possessed moderate acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities.
"This study not only enriches the chemical diversity of mexicanolide-type limonoids in the Meliaceae family but also forms a basis for the discovery of bioactive natural products from Meliaceae herbs," said Prof. Xu Youkai, correspondence author of the study.
More information: Dong-Hua Cao et al. Mexicanolide-type limonoids from the twigs and leaves of Cipadessa baccifera, Phytochemistry (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112449
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences