Researchers have identified areas in the brain that anticipate joy and fear and say they battle it out when a big decision is to be made.
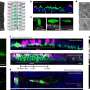
A study by Stanford University scientists Brian Knutson and Camelia Kuhnen highlighted two specific areas of the brain: the dopamine producing nucleus accumbens, which pumps when pleasure is on the horizon, and the anterior insula, which becomes active when a person gets anxious.
The scientists had 20 volunteers play a game with a cash reward, science magazine Nature reports.
When the anterior insula won the battle the participants made safe choices, the study showed. They took risks after dopamine started flowing.
University of California, San Diego, scientist Martin Paulus said the question that needs to be answered now is: When and why does one part of the brain beat the other?
Copyright 2005 by United Press International