Last update:
Biology news

Study identifies best bioenergy crops for sustainable aviation fuels by US region, policy goals
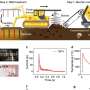
Researchers analyzed the financial and environmental costs and benefits of four biofuels crops used to produce sustainable aviation fuels in the U.S. They found that each feedstock—corn stover, energy sorghum, miscanthus ...
Biotechnology
50 minutes ago
0
0

One elephant can sustain more than 2 million dung beetles in east African savannas, study finds
How many dung beetles are there in East Africa? That question inspired a research project more than 20 years ago when Frank Krell was a research entomologist with the Natural History Museum London. Throughout a three-year-long ...
Plants & Animals
50 minutes ago
0
0

Woodchip bioreactor helps reduce pesticide run-off from horticulture greenhouses
Pesticides seeping out of intensive horticulture into waterways have long-concerned NSW north coast communities. Now a new Southern Cross University study provides evidence that bioreactors can significantly limit this toxic ...
Ecology
40 minutes ago
0
0

Now entering their adult phase, spotted lanternflies are headed into their invasive peak
As you head out on summer adventures this month, make sure that an unwanted guest isn't traveling with you.
Plants & Animals
6 minutes ago
0
0

Counter-drug strategies in Central America are worsening deforestation, threatening many species of birds
Activities associated with cocaine trafficking threaten two-thirds of the most important landscapes in Central America for 196 forest bird species, including 67 migratory species. This is the key takeaway from a study that ...
Ecology
1 hour ago
0
0

Study shows egg-laying mammals are unique, inside and out
The identification of a key gene in monotremes has increased our understanding of why the stomachs of platypuses and echidnas are atypically small, non-acidic, and, in the instance of platypuses, lack a pyloric sphincter.
Plants & Animals
2 hours ago
0
2
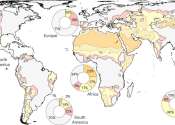
Natural drylands grossly under-protected: Study predicts major threats due to human land-use conversion
Drylands cover about 42% of the Earth's land surface and are increasingly threatened by human land-use pressures like agriculture, alternative energy sources, overgrazing and climate change. Up to a third of the global human ...
Ecology
3 hours ago
0
0

Lethal bird flu could decimate Oceania's birds—from vigilance to vaccines, here's what Australia is doing to prepare
Avian influenza viruses have infected the world's birds for millennia. We first became aware of them in the 19th century, when mass deaths of poultry triggered interest in what was then called "fowl plague."
Plants & Animals
2 hours ago
0
1

Mathematical models used to calculate speed of disease spread in early ocean travel
Two scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles, have developed a way to calculate the approximate speed of disease spread between distant places via ocean travel hundreds of years ago.

Researchers explore a single cell using advanced X-ray imaging techniques
Every plant, animal, and person is a rich microcosm of tiny, specialized cells. These cells are worlds unto themselves, each with their own unique parts and processes that elude the naked eye.
Cell & Microbiology
3 hours ago
0
0

Fruit fly post-mating behavior controlled by male-derived peptide via command neurons, finds study
Scientists have succeeded in pinpointing the neurons within a female fruit fly's brain that respond to signals from the male during mating.
Plants & Animals
3 hours ago
0
1

New rapid method for determining virus infectivity
A new method that can rapidly determine whether a virus is infectious or non-infectious could revolutionize the response to future pandemics.
Molecular & Computational biology
10 hours ago
0
23

Researchers elucidate biogeographic context of human evolution in East African Rift System
Ignacio A. Lazagabaster, a Ramón y Cajal researcher at the Centro Nacional de Investigación sobre la Evolución Humana (CENIEH), is part of the international team that has published a study of the biogeographic context ...
Evolution
3 hours ago
0
0

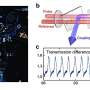
Smart guide RNAs: Researchers use logic gate-based decision-making to construct circuits that control genes
Researchers have transformed guide RNAs, which direct enzymes, into a smart RNA capable of controlling networks in response to various signals. A research team consisting of Professor Jongmin Kim and Ph.D. candidates Hansol ...
Biotechnology
4 hours ago
0
0

Heat-sensitive trees moving uphill due to rising temperatures, study finds
Trees in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest are migrating in search of more favorable temperatures, with species in mountain forests moving uphill to escape rising heat caused by climate change, a new study reveals.
Plants & Animals
4 hours ago
0
1

Cocaine found in muscle and liver of sharpnose sharks off coast of Rio de Janeiro
A team of marine biologists and ecotoxicologists affiliated with several institutions in Brazil has found cocaine in muscle and liver samples collected from Brazilian Sharpnose sharks harvested off the coast of Rio de Janeiro. ...

Off Ecuador's Galapagos, a former shark-poaching ship's new mission
When Ecuador's navy seized a Chinese-flagged ship off the Galapagos Islands in 2017, its hold brimmed with tons and tons of poached fish, many of them threatened species like hammerhead and thresher sharks.
Ecology
9 hours ago
0
0

Discovery of Piezo1's new signaling mechanism may aid search for better pain and itch treatments
The human body's sense of touch is so important it can be found throughout the body, not just on the skin. Two tiny sensors of touch, Piezo1 and Piezo2, signal the lightest pressures and can be found monitoring the circulatory ...
Cell & Microbiology
21 hours ago
0
18

Ciliated eukaryotes study offers simple, versatile method for tubulin staining
Ciliates, a group of single-celled ciliated eukaryotes, have been studied since the dawn of light microscopy, with over 10,000 species described. Cilia are the key feature of ciliates and contribute to their diversity. They ...
Cell & Microbiology
22 hours ago
0
63
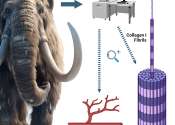
Nanoscopic imaging aids in understanding protein, tissue preservation in ancient bones
A pilot study from North Carolina State University shows that nanoscopic 3D imaging of ancient bone not only provides further insight into the changes soft tissues undergo during fossilization, it also has potential as a ...
Biotechnology
23 hours ago
0
79
More news

Q&A: How machine learning is propelling structural biology
Comprehensive evaluation identifies top finger lime varieties for commercial and ornamental use

Understanding how a red seaweed reduces methane emissions from cows

Genetic breeding offers new method for mosquito population control
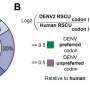
Scientists uncover fundamental rules for how dengue virus infects its mosquito and human hosts
Not everything that tastes bitter is potentially harmful—but why?

Ecologists discover rare fiddler crab species on Hong Kong coast
Other news

Spontaneous supercrystal discovered in switching metal-insulator

Chemists develop test to track crucial edits to RNA

Scientists say sun's influence penetrates into deep Earth
Expiring medications could pose challenge on long space missions

New car smell reaches toxic levels on hot days, researchers find
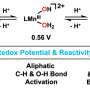
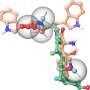
Nature-inspired novel catalyst paves the way for efficient hydrocarbon decomposition

Chinese lunar probe finds water in moon samples
It's not just humans—bacteria also have memory, study suggests

Transient structure in fly leg holds clue to insect shape formation

Researchers work to change perception of weeds in Georgia
'New El Niño' discovered south of the equator