This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Not everything that tastes bitter is potentially harmful—but why?
A bitter taste is traditionally considered a warning sign of potentially toxic substances. But not all bitter substances are harmful. For example, some peptides and free amino acids taste bitter, even though they are non-toxic, nutritious and sometimes even vital for humans.
A new study by the Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology at the Technical University of Munich now offers the first explanation for this seemingly paradoxical phenomenon. The research is published in the journal Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.
In general, our sense of taste helps us to make food choices. Of the five basic tastes, sweet and umami indicate that a food is rich in energy and nutritious. Our sense of salt helps us to keep our electrolyte balance in equilibrium. Sour flavors can warn us of unripe or spoiled food, bitter ones of potentially toxic substances.
In view of numerous toxic plant substances such as strychnine from nux vomica or hydrogen cyanide from manioc, this seems to make sense. And it is also plausible that babies and toddlers in particular reject bitter foods. Even small amounts of such toxic substances are harmful to them.
Protein fragments as bitter as gall
However, not everything that tastes bitter is dangerous, and some can actually be nutritious. An interdisciplinary research team led by molecular biologist Maik Behrens has now investigated the reasons for this seemingly contradictory phenomenon for the first time.
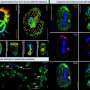
Using an established cellular test system, the Leibniz team discovered that five of the approximately 25 human bitter taste receptor types react to free amino acids and peptides as well as to bile acids. The former are produced during the breakdown of proteins and are abundant in fermented foods such as cream cheese or protein shakes.
Bile acids, on the other hand, play virtually no role as a food component, but fulfill their own functions in the body. They could therefore be considered as activators of endogenous bitter receptors, which are located on intestinal and blood cells, for example.
Explanation: Similar structural features
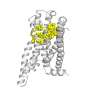
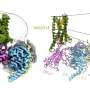
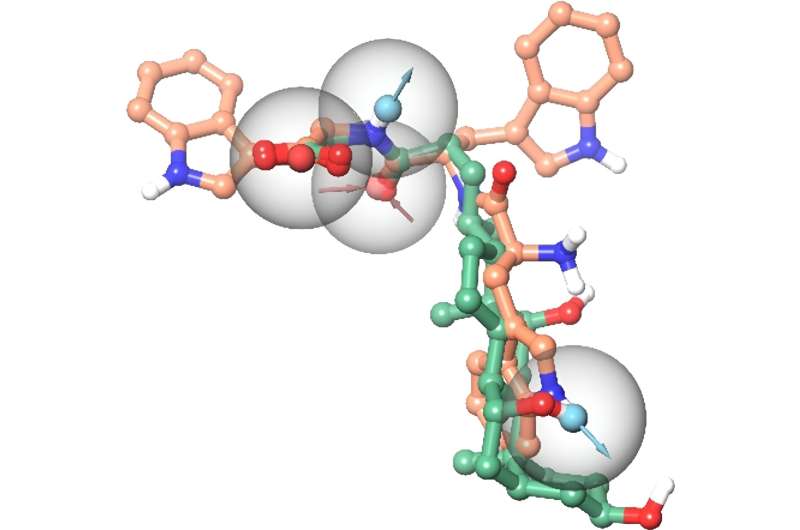
"Interestingly, our modeling experiments show that a certain bitter-tasting peptide can adopt a functionally active 3D shape similar to that of bile acids inside the receptor binding pocket. This coincidental similarity could explain why the same set of the bitter taste receptors react to both groups of substances," explains bioinformatician Antonella Di Pizio.
First author Silvia Schäfer adds, "Our genetic analyses also show that the ability to recognize both bile acids and peptides is highly conserved in three of the bitter taste receptor types and can be traced back to amphibians. This again indicates that at least the recognition of one of the two substance groups is important across species."
"Bile acids and bitter taste receptors existed millions of years before the typical bitter substances of today's flowering plants and long before humans—in fish, for example. This supports the hypothesis that bitter taste receptors originally also regulated important physiological processes and not just warned against toxic substances," explains Behrens.
"Our findings provide new insights into the complex systems of taste perception and suggest that bitter receptors play additional, as yet unknown roles in human health that go beyond their function in food selection."
More information: Silvia Schaefer et al, Membrane-bound chemoreception of bitter bile acids and peptides is mediated by the same subset of bitter taste receptors, Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05202-6
Journal information: Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
Provided by Leibniz Institute for Food Systems Biology