This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Domesticating plants impacts their microbiome, study finds
New research led by the University of Oxford indicates that human domestication of crops can alter the communities of microorganisms that are associated with plants. Intriguingly, independent domestication events were found to have similar impacts on the plant microbiome. The results have been published today in Current Biology.
Lead researcher Dr. Riccardo Soldan (Department of Biology, University of Oxford) said, "Our study provides evidence that regardless of where and how domestication took place, domesticated plants have microbial communities that distinguish them from their wild counterparts.
"This knowledge is important because if we know that a certain domesticated crop species consistently associates with specific microbes, one day we might be able to engineer these communities to deliver positive effects to the host plant."
As microorganisms can have numerous beneficial effects on host plants, such as enhancing growth, stress tolerance, and drought or disease resistance, these findings could ultimately help inform microbe-based approaches to improve crop yields and food security.
For instance, previous work by the research team suggests that domestication may have reduced the ability of crop plants to recruit microorganisms that enhance disease resistance.
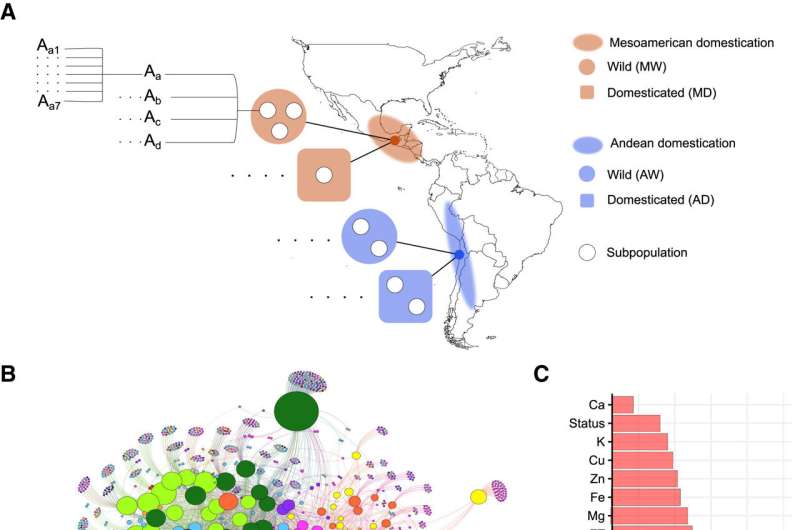
In the new study, the researchers analyzed the microbial communities associated with two crop species that are known to have been domesticated independently multiple times in Mesoamerica and South America: Phaseolus vulgaris (common bean) and Phaseolus lunatus (lima bean). This meant they had a series of replicates for an event that lasted thousands of years.
As the researchers wanted to understand whether any changes in the microbiome were linked to plant traits that were subject to selection by humans during domestication, they focused on microbes associated with seeds.
In seed crops, such as beans, seeds have undergone significant changes during domestication. For example, domesticated bean seeds are significantly larger compared with their wild relatives and have different mineral contents (linked to improved seed quality and cooking properties).
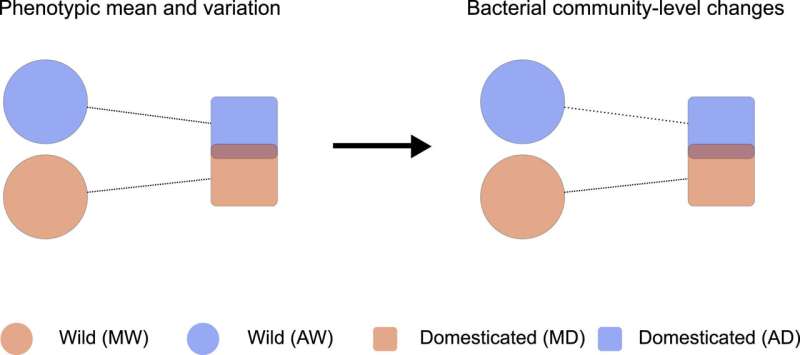
Using statistical and machine learning approaches, the researchers found significant differences in the composition of the microbial communities associated with beans from the wild and domesticated plants.
Furthermore, these changes in microbiome abundance and composition correlated with changes in seed mineral content across multiple domestication events. In particular, reduced calcium concentrations in domesticated P. vulgaris seeds, which may have been selected for as a consequence of selection for improved cooking properties, showed a notable correlation with changes in microbiome composition.
The principal investigator, Professor Gail Preston (Department of Biology, University of Oxford) commented, "Our results provide evidence that the similarities in the microbial communities of independently domesticated plants can be partially explained by the fact that domesticated plants have closely matched plant traits.
"In this case, independent domestication processes selecting for bigger and better seeds in two different regions of the Americas shaped the seed microbiome in similar ways. Understanding the factors that shape microbial communities in wild and domesticated plants could open up exciting opportunities to modify the composition of domesticated crop microbiomes to increase resilience and improve productivity."
In future work, the research team intends to investigate the effect of domestication on other plant traits and on a wider range of crop species. A key question is whether there are beneficial traits present in wild species that act to recruit a diverse and health-promoting microbiome that could be reintroduced into domesticated crops.
More information: Riccardo Soldan et al, Consistent effects of independent domestication events on the plant microbiota, Current Biology (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.12.056
Journal information: Current Biology
Provided by University of Oxford