New concept of fuel cell for efficiency and environment
The Center for Nanoparticle Research at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) has succeeded in proposing a new method to enhance fuel cell efficiency with the simultaneous removal of toxic heavy metal ions.
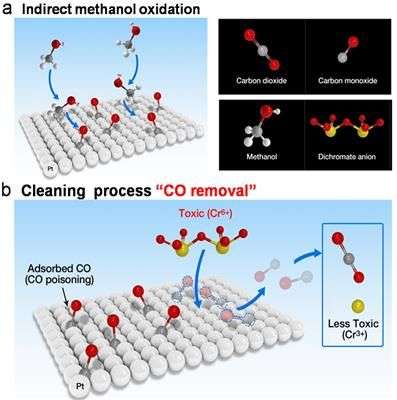
The direct methanol fuel cell (DFMC) has been a promising energy conversion device for electrical vehicles and portable devices. However, the inevitable carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is one of the main factors reducing its performance. Furthermore, the hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) also present, is a harmfully toxic, carcinogenic heavy metal in the aquatic environment.
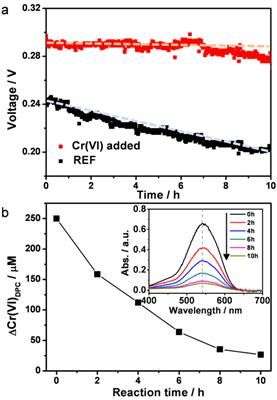
The research team applied the Cr (VI) as a type of "CO scavenger" to the DMFC. Their new method not only uses the redox process to clean the platinum electrode surface by transforming CO into CO2 , but also allows for the Cr (VI) to convert into Cr (III), which is a much less toxic oxidation state and even a micronutrient. As a result, the potential maintained a nearly constant value of up to 10 hours and the presence of Cr (VI) was completely absent. Moreover, it enhances the maximum power density by 20% at 70℃.
"Fuel cells have presented obstacles such as low performance and CO poisoning which have prevented them from becoming possible, next generation energy sources until now," explains Professor Yung-Eun Sung, both a group leader of the Center for Nanoparticle Research at IBS and the professor of the School of Chemical and Biological Engineering at the Seoul National University. "This new hybrid fuel cell technology is expected to propel the deployment of direct methanol fuel cells."
More information: Dong Young Chung, Hyoung-il Kim, Young-Hoon Chung, Myeong Jae Lee, Sung Jong Yoo, Alok D. Bokare and Wonyong Choi, Yung-Eun Sung (2014). "Inhibition of CO poisoning on Pt catalyst coupled with the reduction of toxic hexavalent chromium in a dual-functional fuel cell." Scientific Reports, 4, 7450, DOI: 10.1038/srep07450
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Institute for Basic Science