Researchers use a novel approach to identify a transport protein in mycobacteria
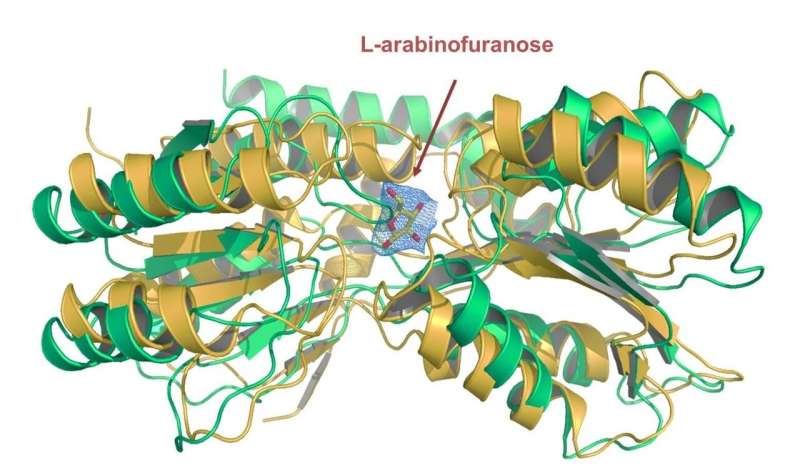
A team headed by Dr. Claudia Jessen-Trefzer of the University of Freiburg's Institute for Pharmaceuticals Sciences has identified a transport protein in mycobacteria that is responsible for the uptake of the nutrient L-arabinofuranose. The lead authors of the study, Miaomiao Li of the Institute for Pharmaceuticals Sciences, Christoph Müller of the Institute for Biochemistry and Klemens Fröhlich of the Institute of Molecular Medicine and Cell Research at the University of Freiburg, used a novel approach that could simplify the identification of transport proteins in mycobacteria in the future. This class of proteins could play a key role in the development of new types of medications to tackle mycobacteria and treat diseases like tuberculosis in humans. The researchers' study is published in the journal Cell Chemical Biology.
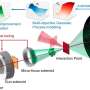
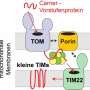
Transport proteins are located in the membrane of the cell and are responsible for absorbing nutrients into the cell and expelling toxic substances out of it. They therefore drive processes which are vital to the cell's survival. Until now, little was known about the proteins because their chemical properties make them difficult to examine. The Freiburg researchers characterized the protein on the basis of its substrate, the nutrient L-arabinose, with which the protein bonds. A subgroup of the bacterium, Mycobacterium smegmatis, served as the model organism.
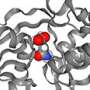
The team developed a method in which they carried out gene expression - the targeted expression of genes and the translation into proteins - via the substrate. Then they investigated the proteins isolated from the membrane using mass spectrometry. This provided the Freiburg researchers with a relatively simple way of identifying the transport proteins which are responsible for absorbing a certain nutrient. In addition, they were able to identify the L-arabinofuranose transporter whose characteristics could be determined with protein crystallography. The team managed to vastly simplify the identification of transport proteins in mycobacteria, thereby contributing to the search for potential target proteins for antibiotics development.
More information: Miaomiao Li et al. Detection and Characterization of a Mycobacterial L-Arabinofuranose ABC Transporter Identified with a Rapid Lipoproteomics Protocol, Cell Chemical Biology (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.03.002
Journal information: Cell Chemical Biology
Provided by Albert Ludwigs University of Freiburg