This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers convert alcohols into aldehydes without solvents by using gold-coated milling vessels
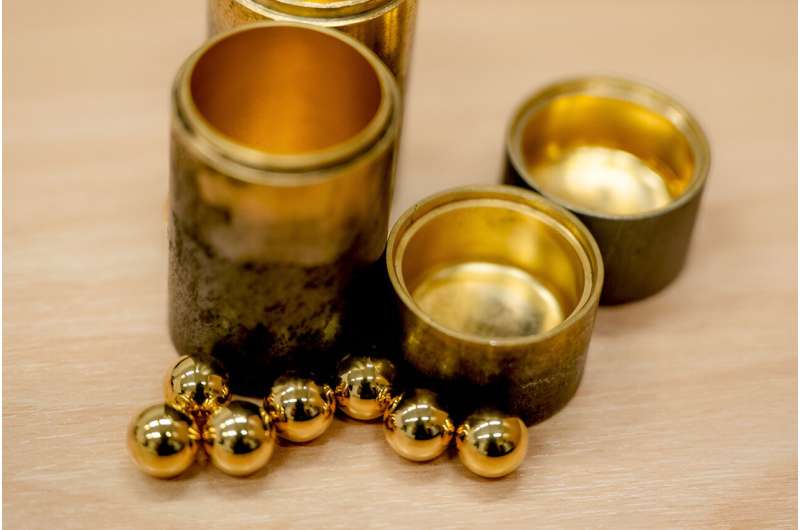

A gold-coated milling vessel for ball mills proved to be a real marvel in the research work by Inorganic Chemistry at Ruhr University Bochum, Germany. Without any solvents or environmentally harmful chemicals, the team led by Professor Lars Borchardt was able to use the vessel to convert alcohols into aldehydes.
The catalytic reaction takes place at the gold surface and is mechanically driven. The vessel can be reused multiple times.
"This opens up new prospects for the use of gold in catalysis and shows how traditional materials can contribute to solving modern environmental problems in an innovative way," says Borchardt. The team has published their research in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Aldehydes are essential compounds in the chemical industry and are used in the manufacture of medications, vitamins, and fragrances. The selective oxidation of alcohols into aldehydes without secondary reactions is thus of great importance.
Overoxidation often occurs with many conventional methods, causing unwanted byproducts such as carboxylic acid and esters to be formed. Traditional alcohol oxidation methods also often require the use of solvents and environmentally harmful chemicals.
They not only produce harmful waste but also pose significant health risks for users. In addition, high temperatures and pressures are often used that can cause temperature-sensitive substrates to break down.
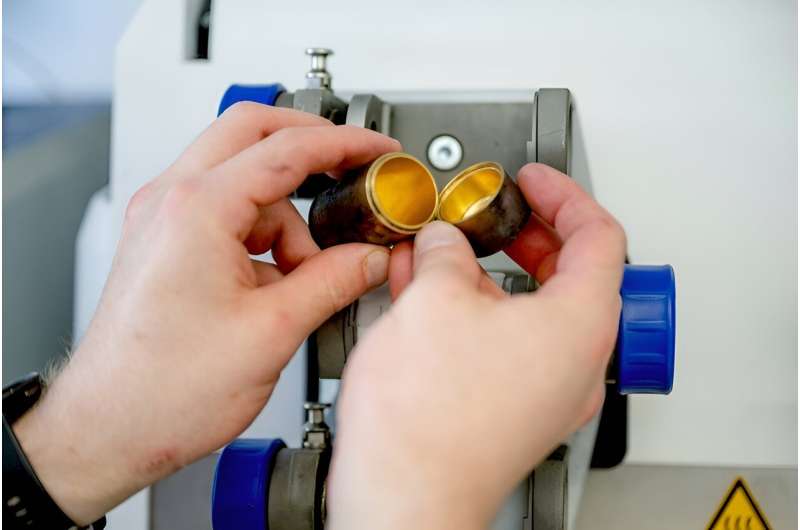

Reusable vessels
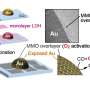
The Bochum team instead uses mechanochemistry: Ball mills, usually used to grind up materials, are used to conduct chemical reactions. The crucial breakthrough lies in the use of grinding vessels coated with a thin layer of gold just a few nanometers thick.
"As we discovered that the reaction exclusively takes place at the gold surface, we were able to limit ourselves to the smallest quantities of the precious metal by simply coating the grinding vessel," says lead author Maximilian Wohlgemuth. "The vessels can also be reused over several reactions."
The catalytic reaction takes place directly in the ball mill, without the use of harmful solvents and in mild conditions, which retains the integrity of the substrates and increases energy efficiency.
"Our method produces significantly less waste and dispenses with the costly production of molecular gold compounds or gold nanoparticles," summarizes Wohlgemuth. This makes the process not just more sustainable but also more cost-effective.
The introduction of gold as a catalyst in mechanochemical processes has the potential for use in many areas of chemistry. "Our results could pave the way for further research and developments based on the use of precious metals in environmentally friendly processes," says Borchardt.
"The combination of high efficiency, low environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness makes our method a promising approach for the future of chemistry."
More information: Maximilian Wohlgemuth et al, Solid‐State Oxidation of Alcohols in Gold‐Coated Milling Vessels via Direct Mechanocatalysis, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2024). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202405342
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided by Ruhr-Universitaet-Bochum