This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Supercharging fuel cells with caffeine
With global goals set on transitioning away from fossil fuels, fuel cells stand out as a promising carbon-free energy source. Comprising an anode and a cathode separated by an electrolyte, fuel cells convert the chemical energy of fuel directly into electricity. The anode receives the fuel, while an oxidant, typically oxygen from the air, is introduced at the cathode.
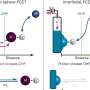
In a hydrogen fuel cell, hydrogen undergoes oxidation at the anode, producing hydrogen ions and electrons. The ions move through the electrolyte to the cathode, and electrons flow through an external circuit, generating electricity. At the cathode, oxygen combines with the hydrogen ions and electrons, resulting in water as the sole byproduct.
However, the presence of water affects the performance of the fuel cell. It reacts with the platinum (Pt) catalyst, forming a layer of platinum hydroxide (PtOH) on the electrode, which obstructs the efficient catalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), leading to energy losses. To maintain efficient operation, fuel cells require a high Pt loading, which significantly increases the costs of fuel cells.
Now, in a study published in the journal Communications Chemistry on February 3, 2024, Professor Nagahiro Hoshi, along with Masashi Nakamura, Ryuta Kubo, and Rui Suzuki, all from the Graduate School of Engineering at Chiba University, Japan, have found that adding caffeine to certain platinum electrodes can increase the activity of the ORR. This discovery has the potential to reduce platinum requirements, making fuel cells more affordable and efficient.
"Caffeine, one of the chemicals contained in coffee, enhances the activity of a fuel cell reaction 11-fold on a well-defined Pt electrode of which atomic arrangement has a hexagonal structure," says Prof. Hoshi.
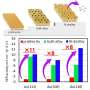
To assess caffeine's impact on the ORR, researchers measured current flow through platinum electrodes immersed in an electrolyte containing caffeine. These platinum electrodes had surface atoms arranged in specific directions, namely (111), (110), and (100).
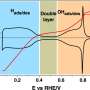
There was a notable improvement in the electrode's ORR activity with an increase in caffeine concentration in the electrolyte. Caffeine, when present, adsorbs onto the electrode's surface, effectively preventing hydrogen adsorption and the formation of Pt oxide on the electrode. However, the effect of the caffeine depended on the orientation of the platinum atoms on the electrode's surface.
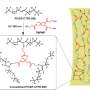
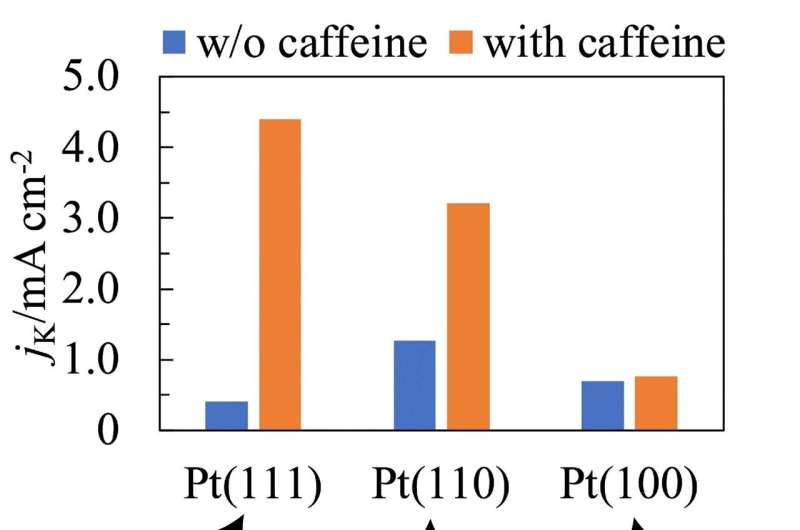
At a caffeine molar concentration of 1 × 10−6, the ORR activity on Pt(111) and Pt(110) increased by 11 and 2.5 times, respectively, with no noticeable effect on Pt(100). To understand this difference, the researchers investigated the molecular orientation of caffeine on the electrode surface using Infrared Reflection Absorption Spectroscopy.
They found that caffeine gets absorbed on Pt(111) and Pt(110) surfaces with its molecular plane perpendicular to the surface. However, on Pt(100), steric hindrances cause it to be attached with its molecular plane tilted relative to the surface of the electrode.
"The increased ORR activity of Pt(111) and Pt(110) was attributed to the decreased PtOH coverage and lower steric hindrance of the adsorbed caffeine. Conversely, for Pt(100), the effect of decreasing PtOH was counteracted by the steric hindrance of the adsorbed caffeine, and thus caffeine did not affect the ORR activity," explains Prof. Hoshi.
Unlike batteries with limited lifespans, fuel cells can generate power as long as fuel is supplied, making them suitable for various applications, including vehicles, buildings, and space missions. The proposed method has the potential to improve the designs of fuel cells and lead to their widespread use.
More information: Nagahiro Hoshi et al, Enhanced oxygen reduction reaction on caffeine-modified platinum single-crystal electrodes, Communications Chemistry (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s42004-024-01113-6
Journal information: Communications Chemistry
Provided by Chiba University