This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Energy-saving electrochemical hydrogen production via co-generative strategies in hybrid water electrolysis
With the increase in global energy demand and environmental pollution, the development of sustainable energy to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels (such as oil, natural gas, and coal) has become the key to achieving sustainable development of human society.
Hydrogen energy is considered the ideal alternative energy because of its high energy density, pollution-free combustion, and various application forms.
Hydrogen production from water splitting includes cathodic hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and anodic oxygen evolution reaction (OER), which has the characteristics of green environmental protection, flexible production, and high purity, and is one of the ideal green production technologies. However, the intrinsic slow kinetics of the anodic oxygen evolution reaction severely results in low hydrogen production efficiency of the cathode.
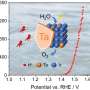
In addition, during the process of water electrolysis, highly oxidizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) will be produced, reducing the life of the film for electrolytic water and hindering the practical application of electrolytic water technology. Therefore, it is urgent to develop new high-efficiency, stable, and high-value-added electrolytic water catalysts.
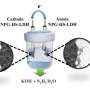
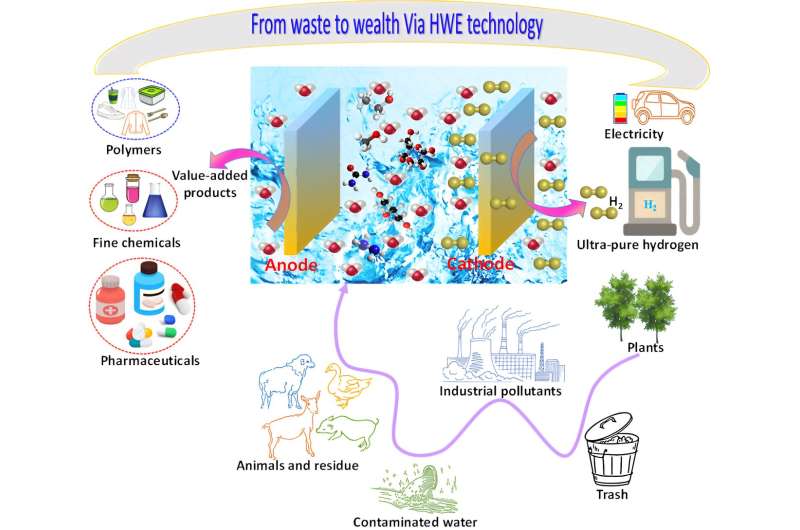
The hybrid water electrolysis (HWE) configuration that combines thermodynamically favorable oxidation reaction processes at the anode and HER at the cathode comes into the spot as a particularly attractive alternative to maximize H2 production.
More importantly, substituting the sluggish OER process with thermodynamically more favorable oxidation reactions affords ground-breaking for enriching highly efficient energy-saving H2 production, meanwhile enabling additional functionalities such as purifying industrial wastewater and creating high-value-added chemicals.
Hence, it is requisite to nominate suitable synergistic electrocatalysis configurations based on electrochemical precepts of electro-coupled catalytic processes.
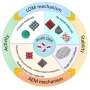
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Qinfang Zhang from Yancheng Institute of Technology, China, reviewed some key guidelines for the discovery of efficient multi-functional hybrid water electrolysis (HWE) systems for co-generation of energy-saving H2 and high value-added products. An overview of the HWE system is presented first, accompanied by a discussion on the design and engineering of high reactive/selective/stable electrodes/electrocatalysts for anodic oxidation of organic/biomass substrates.
The in-depth understanding of possible reaction mechanisms from both experimental and theoretical perspectives is elucidated to promote the efficiency of synergistic electrocatalysis. The recent research breakthroughs in the field of HWE technology are emphatically reviewed, providing new room for low-voltage H2 generation from waste products and renewable feedstock.
Proposing the prospects of existing challenges with some opportunities for future research directions is also presented in this work. The results were published in the Chinese Journal of Catalysis.
More information: Diab khalafallah et al, Energy-saving electrochemical hydrogen production via co-generative strategies in hybrid water electrolysis: Recent advances and perspectives, Chinese Journal of Catalysis (2023). DOI: 10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64544-9
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences