This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers develop new selective emitter based on iridium for thermophotovoltaics
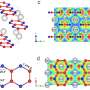
Researchers from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon, together with the Technical University of Hamburg and Aalborg University, have developed a new selective emitter based on iridium for thermophotovoltaics. Iridium was thus used for the first time as a material for an emitter, and in the experiments, it showed particular endurance at high temperatures around 1,000°C. Their study results were published in the journal Advanced Materials and open up new perspectives for producing electricity from heat.
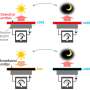
The conversion of heat into electricity is the principle of thermophotovoltaics. To make the heat efficiently usable in the form of radiant energy, so-called selective emitters are needed. They sit between the heat source and the photovoltaic cell and emit only a certain part of the radiation while suppressing the other.
The challenge here is that the conversion of heat into electricity takes place at high temperatures around 1,000°C—the emitter must therefore be able to withstand these temperatures without losing the accuracy of its selectivity. The researchers have now succeeded in producing a new emitter based on the resistant metal iridium that can withstand these conditions without losing its effectiveness.
"With iridium, we address both aspects at the same time: selectivity and temperature stability," says Alexander Petrov, who works on optical properties of materials at TUHH. "Selective emitters based on iridium are very good at suppressing unwanted radiation and do not react with oxygen. Iridium is a precious metal like gold, but suitable for high-temperature applications."
"By avoiding the adverse effects of oxidation, we have unlocked the potential for more efficient and sustainable systems," reports Gnanavel Vaidhyanathan Krishnamurthy, lead author of the study and a scientist at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon. "This innovation opens the doors to new possibilities in waste heat recovery, solar thermal power generation and beyond."
The emitter's function
In thermophotovoltaics, as in photovoltaics, radiant energy is converted into electricity by a photovoltaic cell. However, in thermophotovoltaics the radiant energy does not come from the sun, but from a heat source, such as is used in the steel industry. The emitter is located between the heat source and the solar cell. It consists of several very thin layers (metal and oxide alternately), which should remain unchanged at high temperatures to enable heat to be converted into electricity. For this purpose, it ideally emits only short-wave photons and suppresses long-wave ones—it thus has a selective effect. This is important because the photovoltaic cell is not able to convert the long-wave radiation into electricity.
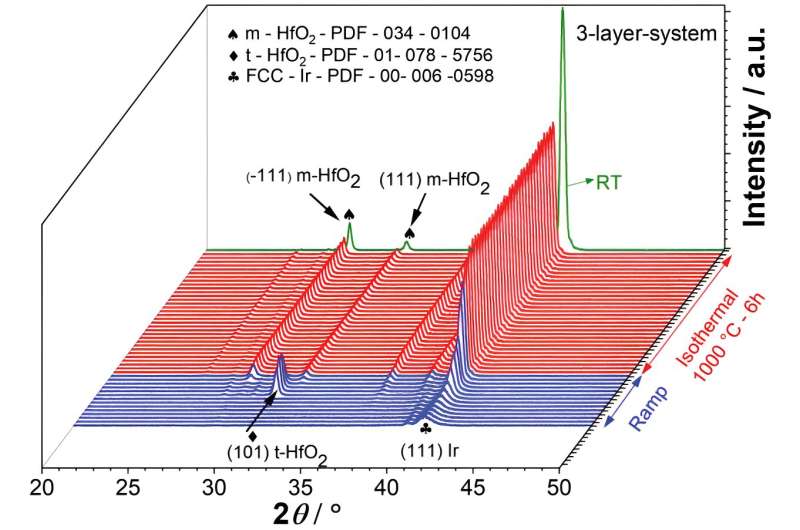
At high temperatures, however, most metals oxidize and the function of the emitter fails. As the researchers were able to show, the newly developed selective emitter made of iridium and hafnium oxide retains its function completely over 100 hours at 1,000°C—the metal withstands the demanding challenges without any losses, as the researchers were able to show through X-ray examinations. The successful development of selective emitters based on iridium is an important step towards the further development of thermophotovoltaics.
In the transition to renewable energy, securing a constant power supply is of great importance. Thermophotovoltaics could not only generate electricity from industrial waste heat, but also make an important contribution to the conversion of the energy supply to renewable energies. Here, the energy generated by photovoltaics and wind turbines, which naturally fluctuates over time, is temporarily stored in heat reservoirs in order to extract it again later—when the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing—and convert it into electrical energy, which is then continuously available, by means of thermophotovoltaics, and in this way stabilize the energy grids.
More information: Gnanavel Vaidhyanathan Krishnamurthy et al, Iridium‐Based Selective Emitters for Thermophotovoltaic Applications, Advanced Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202305922
Journal information: Advanced Materials
Provided by Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres