Bacteria generate electricity from methane
Generating power while purifying the environment of greenhouse gases should be achievable using bacteria. In a new publication, microbiologists from Radboud University have demonstrated that it is possible to make methane-consuming bacteria generate power in the lab. The study will be published in Frontiers in Microbiology on April 12.
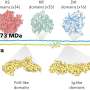
The bacteria, Candidatus methanoperedens, use methane to grow and naturally occur in fresh water such as ditches and lakes. In the Netherlands, the bacteria mostly thrive in locations where the surface and groundwater are contaminated with nitrogen, as they require nitrate to break down methane.
The researchers initially wanted to know more about the conversion processes occurring in the microorganism. In addition, they were also curious whether it would be possible to use it to generate power. "This could be very useful for the energy sector," says microbiologist and author Cornelia Welte. "In the current biogas installations, methane is produced by microorganisms and subsequently burnt, which drives a turbine, thus generating power. Less than half of the biogas is converted into power, and this is the maximum achievable capacity. We want to evaluate whether we can do better using microorganisms."
A kind of battery
Fellow microbiologists from Nijmegen have previously shown that it is possible to generate power using anammox bacteria that use ammonium during the process instead of methane. "The process in these bacteria is basically the same," says microbiologist Heleen Ouboter. "We create a kind of battery with two terminals, where one of these is a biological terminal and the other one is a chemical terminal. We grow the bacteria on one of the electrodes, to which the bacteria donate electrons resulting from the conversion of methane."
Through this approach, the researchers managed to convert 31 percent of the methane into electricity, but they aim at higher efficiencies. "We will continue focusing on improving the system," Welte says.
More information: Heleen T. Ouboter et al, Methane-Dependent Extracellular Electron Transfer at the Bioanode by the Anaerobic Archaeal Methanotroph "Candidatus Methanoperedens", Frontiers in Microbiology (2022). DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.820989
Journal information: Frontiers in Microbiology
Provided by Radboud University Nijmegen