New study models path for achieving state's renewable energy targets

The Hawai'i Natural Energy Institute (HNEI) at UH Mānoa, in partnership with GE Energy Consulting, has completed an analysis identifying various scenarios that would allow the islands of O'ahu and Maui to surpass Hawai'i's 2020 renewable energy targets while lowering electricity costs.
The study evaluated various mixes of renewable energy generation (primarily wind and solar), different island-interconnection strategies, and changes to utility operations to identify cost-effective pathways to meet the state's Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) targets. Funding for the Hawai'i RPS Study was provided by the U.S. Department of Energy and the State of Hawai'i via the Energy Systems Development Special Fund (aka, "barrel tax").
"This analysis shows that Hawai'i can cost-effectively achieve and even exceed the 30% goal for 2020 mandated by recent legislation," said John Cole, HNEI project leader. "ACT 97, signed into law earlier this month, also requires 100 percent renewable electrical energy by 2045. This study provides a valuable tool to assess potential pathways to meet this aggressive goal while also maintaining a reliable system for everyone."
Cole added, "The challenge with achieving 100% renewable energy has more to do with how to reliably store and distribute the electricity than with how the electricity is generated. The current grid isn't flexible enough to respond to rapid changes in energy supply or demand, and energy storage is not yet cost effective. Intermittent sources like wind and solar are often 'curtailed' or purposely restricted, which is a waste of good energy."

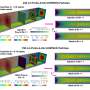
The study, which considered the islands of O'ahu and Maui, used the GE Multi-Area Production Simulation (MAPS) model to simulate the electric power system operation with varying amounts of utility-scale wind and solar, as well as increasing amounts of distributed rooftop solar photovoltaics (PV). The team coordinated with the local utility company to identify and model the generation mix expected to be in place by 2020.
A variety of utility operational changes including reduced minimums on thermal units, thermal unit cycling, demand response, alternate fuels (e.g. Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)) and adjustments to ancillary service procurement were evaluated in the analysis. Another GE model, the Multi-Area Reliability Simulation (MARS), was used to assess system reliability while operating with a significant contribution of intermittent wind and solar generation.
In addition to estimating production cost savings as reported in previous studies, this work also developed preliminary economic models to estimate the cost of additional power purchases, new grid equipment and operational changes. This work, did not consider distribution level impacts or limitations, or the costs associated with changes to the distribution system.
"This modeling provides an independent look at the utility system and how changes to it and its operations can affect its costs and ability to accept additional renewables," said Dr. Richard Rocheleau, HNEI Director. "The report and additional analyses that build upon it will provide regulators and other stakeholders with valuable information as we continue reducing our dependence on fossil fuels."
Key findings of the study include:
- High levels of intermittent renewable energy generation with minimal curtailment can be achieved with modifications to electric system operations and infrastructure expected by 2020. With these changes, the islands of O'ahu and Maui can surpass the 2020 RPS goal while lowering electricity costs and increasing the reliability of the grid with or without island interconnection.
- Balanced growth of wind and utility-scale and distributed solar was shown to help reduce the aggregate variability and intermittency and the need for ancillary services on the grid relative to continued expansion of a single resource type.
- The use of natural gas as a transition fuel has the potential to substantially lower the cost of electricity, depending on cost projections for LNG and oil. The price will be dependent on the volume of LNG consumed, hence any cost benefit decreases as renewable penetration increases.
- Increased use of energy efficiency, demand response, and storage will be needed to maintain grid reliability with fewer thermal generators on the system, as is projected by the utility.
- Inter-island transmission can facilitate more efficient use of resources, contribute to increased grid reliability, and enable increased renewable penetration by providing expanded siting options.
HNEI and GE are continuing this work, including analysis of frequency stability at both the system and distribution levels with larger amounts of wind and solar; a more detailed evaluation of the value (cost/benefit) of mitigation measures including advanced grid technologies such as storage, demand response and other ancillary services; an assessment of the impact of advanced transportation systems such as electric, and fuel-cell electric vehicles; and the risk of fuel price volatility.
More information: The RPS Study Report is available here: www.hnei.hawaii.edu/projects/hawaii-rps-study
Provided by University of Hawaii at Manoa