Last update:
Nanotechnology news

Rare earth single atoms enhance manganese oxide's electrochemical oxygen evolution
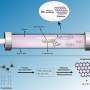
An international group of researchers has developed a novel approach that enhances the efficiency of the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), a key process in renewable energy technologies. By introducing rare earth single atoms ...
Nanomaterials
5 hours ago
0
1

High-speed atomic force microscopy reveals dynamic behavior of brain receptors
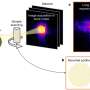
Researchers at the Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, used high-speed atomic force microscopy to observe dynamic changes in AMPA receptors, which are vital for brain communication. Their findings, ...
Bio & Medicine
5 hours ago
0
11

How much microplastic are you drinking? New tool can tell you in minutes
Micro- and nanoplastics are in our food, water and the air we breathe. They are showing up in our bodies, from testicles to brain matter. Now, University of British Columbia researchers have developed a low-cost, portable ...
Bio & Medicine
Aug 27, 2024
0
110

New technique shows promise for mass fabricating an exotic quasi-1D material
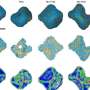
Researchers have fabricated a quasi-one-dimensional van der Waals zirconium telluride thin film, which is a form of a substance that has long promised advances in quantum computing, nano-electronics and other advanced technologies. ...
Nanomaterials
Aug 27, 2024
0
21

Nanotubes get a boost: Liquid-phase synthesis unlocks efficient production
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are known for their remarkable properties, which make them essential in many advanced technologies. Yet, creating these nanotubes efficiently and on a large scale has been a persistent ...
Nanomaterials
Aug 27, 2024
0
9

Manganese nanoparticles can more than double availability of world's potable water, say scientists
Manganese ferrite nanoparticles could lead to a substantial surge in the availability of drinking water globally when used to modify the filtering sheets currently used in water treatment plants, according to scientists.
Nanomaterials
Aug 26, 2024
0
10

Manipulation of nanolight provides new insight for quantum computing and thermal management
A recent study led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers provides fundamental insight into how light, electrons, and crystal vibrations interact in materials. The research has implications for developing on-chip ...
Nanophysics
Aug 26, 2024
0
42

Researchers develop high-entropy non-covalent cyclic peptide glass for smart functional materials
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a sustainable, biodegradable, biorecyclable material: high-entropy non-covalent cyclic peptide (HECP) glass. This ...
Nanomaterials
Aug 26, 2024
0
19

New varactor enhances quantum dot device measurements at millikelvin temperatures
The development of quantum computing systems relies on the ability to rapidly and precisely measure these systems' electrical properties, such as their underlying charge and spin states. These measurements are typically collected ...

Researchers demonstrate metasurfaces that control thermal radiation in unprecedented ways
Researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have experimentally demonstrated that metasurfaces (two-dimensional materials structured at the nanoscale) can precisely control ...
Nanophysics
Aug 23, 2024
0
80

A leap forward in nanotechnology: Growing special micro-crystals for better devices
In a paper published in the journal Advanced Materials, Dr. Atikur Rahman's research group from the Physics department at IISER Pune, India, along with collaborators, report a new way to grow special crystals called CsPbBr3 ...
Nanomaterials
Aug 23, 2024
0
55

For first time, DNA tech offers both data storage and computing functions
Researchers from North Carolina State University and Johns Hopkins University have demonstrated a technology capable of a suite of data storage and computing functions—repeatedly storing, retrieving, computing, erasing ...
Bio & Medicine
Aug 22, 2024
0
209

Advancing nanoscale imaging capabilities with dynamic nuclear polarization
Dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) has revolutionized the field of nanoscale nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), making it possible to study a wider range of materials, biomolecules and complex dynamic processes such as how ...
Nanophysics
Aug 22, 2024
0
11

Engineers design lookalike drug nanocarrier to evade lung's lines of defense
A drug-carrying molecule designed to cure disease by slipping past the lung's natural defenses offers new hope for people with chronic or deadly respiratory diseases, say its creators, researchers in assistant professor Liheng ...
Bio & Medicine
Aug 22, 2024
0
82

High speed, large-area deposition nanofilm production possible with new technique
A Japanese research team led by Professor Minoru Osada from the Institute for Materials and Systems for Sustainability (IMaSS) at Nagoya University has pioneered a method for the high-speed, large-area deposition of two-dimensional ...
Nanomaterials
Aug 22, 2024
0
2

Alzheimer's drug may someday help save lives by inducing a state of 'suspended animation'
Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University report that they were able to successfully put tadpoles of Xenopus laevis frogs into a hibernation-like torpor state using donepezil ...
Bio & Medicine
Aug 22, 2024
0
83

World's first micromachine twists 2D materials at will
Just a few years ago, researchers discovered that changing the angle between two layers of graphene, an atom-thick sheet of carbon, also changed the material's electronic and optical properties. They then learned that a "twist" ...
Nanophysics
Aug 22, 2024
0
147

A world first: Qubit coherence decay traced to thermal dissipation
Physicists from Aalto University in Finland, alongside an international team of collaborators, have theoretically and experimentally shown that superconducting qubit coherence loss can be directly measured as thermal dissipation ...
Nanophysics
Aug 22, 2024
0
45

Novel carbon nanohorn-based treatment enables efficient delivery of drugs in cancer therapy
Cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases to treat due to its complexity and tendency to metastasize (spread into, or invade, nearby tissues or distant places in the body to form new tumors). Traditional therapies, ...
Bio & Medicine
Aug 22, 2024
0
16

CeO₂ nanoparticles: A double-edged sword for aquatic algal life
A new study reveals significant alterations in growth, photosynthetic activity, and gene expression of freshwater algae due to cerium oxide nanoparticles. This research highlights the complex interactions between these microscopic ...
Bio & Medicine
Aug 22, 2024
0
17
Other news

Scientists discover a long-sought global electric field on Earth

'Silent' mutations found to have repercussions beyond their own gene

Dogs understand words from soundboard buttons, study reveals

Bacterial cells transmit 'memories' to offspring, research finds

A way to recover silver from dead solar panels with 98% efficiency

DNA replication in early embryos differs from previous assumptions, study shows

Plant signaling pathways decoded using 'optogenetic' tobacco plants

Breaking open the AI black box, team finds key chemistry for solar energy and beyond