Last update:
Condensed Matter news

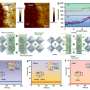
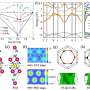
Physicists propose path to faster, more flexible robots
In a May 15 paper released in the journal Physical Review Letters, Virginia Tech physicists revealed a microscopic phenomenon that could greatly improve the performance of soft devices, such as agile flexible robots or microscopic ...
Condensed Matter
May 18, 2024
0
79
Study examines low-permittivity dielectric ceramics for microwave/millimeter-wave communication
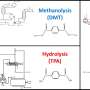
Microwave dielectric ceramics are the cornerstone of wireless communication devices, widely utilized in mobile communications, satellite radar, GPS, Bluetooth, and WLAN applications. Components made from these ceramic materials, ...
Condensed Matter
May 17, 2024
0
2
Researchers suppress non-Hermitian effects via 'fake' magnetic fields
Due to the presence of non-Hermitian components, wave intensities tend to localize at the system boundary, namely the non-Hermitian skin effect. The skin behavior is protected by topology, making it insensitive to minor changes. ...
Condensed Matter
May 17, 2024
0
29
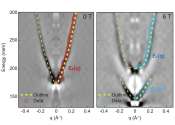
The observation of a Spin Berry curvature-enhanced orbital Zeeman effect in a kagome metal
In solid materials, magnetism generally originates from the alignment of electron spins. For instance, in the ferromagnet iron, the overall net magnetization is prompted by the alignment of spins in the same direction.

Method milestone for quantum physics: Rapid test for topological 2D materials
Topological quantum materials are hailed as a cornerstone of future technological advancements. Yet, validating their exceptional qualities has always been a lengthy process.
Condensed Matter
May 16, 2024
0
37

Researchers make a surprising discovery: Magnetism in a common material for microelectronics
Nickel monosilicide (NiSi) is widely used to connect transistors in semiconductor circuits. Earlier theoretical calculations had incorrectly predicted that NiSi was not magnetic. As a result, researchers had never fully explored ...
Condensed Matter
May 15, 2024
0
10

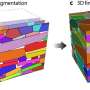
Simulating diffusion using 'kinosons' and machine learning
Researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have recast diffusion in multicomponent alloys as a sum of individual contributions, called "kinosons." Using machine learning to compute the statistical distribution ...
Condensed Matter
May 15, 2024
0
46

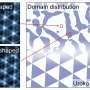
Quantum geometry offers new insights into 'smart' materials with switchable electric polarity
Quantum theorists at the University of British Columbia have proposed a new approach to studying stacking ferroelectricity—spontaneous electric polarization—in layered, two-dimensional lab-grown materials.
Condensed Matter
May 15, 2024
0
73

Scientists raise minimum magnetic field of a single measurement to sub-femtotesla level
A research team has, for the first time, realized the quantum amplification of an extremely weak magnetic field by using dark spin, with the magnetic field magnification exceeding a factor of 5,000 and the single magnetic ...
Condensed Matter
May 15, 2024
0
10

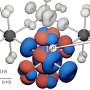
Advancing transistor technology with triply-degenerate semimetal PtBi₂
Despite its promising characteristics in condensed matter physics, the triply-degenerate semimetal PtBi2 has been largely unexplored in practical applications, particularly in semiconductor technology. The main difficulties ...
Condensed Matter
May 14, 2024
0
9

Research team develops electromagnetic wave absorbers with strong absorption and broad effective bandwidth
A research team from the Department of Functional Composites in Composites Research Division at Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS) has successfully developed electromagnetic wave absorbers based on metal-organic ...
Condensed Matter
May 14, 2024
0
25

Research finds drastic changes in thermal conductivity of diamonds under stress
Diamond is the hardest material found in nature—diamond also has the highest thermal conductivity, allowing the most heat to flow through it rapidly.
Condensed Matter
May 14, 2024
0
9

Study shows how light can transform an insulating material into a semimetal
The elements in the periodic table are divided into metals, semimetals and non-metals. The distinction is based on their chemical and physical properties and is determined, in particular, by the movement of electrons and ...
Condensed Matter
May 14, 2024
0
32

Physicists create five-lane superhighway for electrons
MIT physicists and colleagues have created a five-lane superhighway for electrons that could allow ultra-efficient electronics and more. The work, reported in the May 9 issue of Science, is one of several important discoveries ...
Condensed Matter
May 13, 2024
0
465
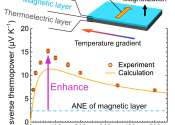
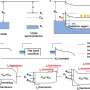
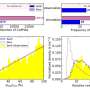
Exceptionally large transverse thermoelectric effect produced by combining thermoelectric and magnetic materials
A NIMS research team has demonstrated for the first time ever that a simple stack of thermoelectric and magnetic material layers can exhibit a substantially larger transverse thermoelectric effect—energy conversion between ...
Condensed Matter
May 13, 2024
0
120

New method unravels the mystery of slow electrons
Slow electrons are used in cancer therapy as well as in microelectronics. It is very hard to observe how they behave in solids. But scientists at TU Wien have made this possible.
Condensed Matter
May 13, 2024
0
6

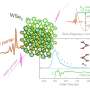
Spectral evidence found for Dirac spinons in a kagome lattice antiferromagnet
A new study, published in a recent issue of Nature Physics, sheds light on the long-anticipated emergence of quasiparticles, akin to the famous Dirac particles obeying the relativistic Dirac equation. These quasiparticles, ...
Condensed Matter
May 13, 2024
0
54

Stable magnetic bundles achieved at room temperature and zero magnetic field
Recently, the research team led by Prof. Du Haifeng from the High Magnetic Field laboratory at Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences achieved stable magnetic bundles at room temperature without ...
Condensed Matter
May 10, 2024
0
142

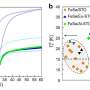
Transforming common soft magnets into next-generation thermoelectric conversion materials with 3-minute heat treatment
A research team from NIMS and Nagoya University has demonstrated that an iron-based amorphous alloy, widely used as a soft magnetic material in transformers and motors, can be transformed into a "transverse" thermoelectric ...
Condensed Matter
May 10, 2024
0
103

New phononics materials may lead to smaller, more powerful wireless devices
What if your earbuds could do everything your smartphone can do already, except better? What sounds a bit like science fiction may actually not be so far off. A new class of synthetic materials could herald the next revolution ...
General Physics
May 9, 2024
0
113
More news

Topological phonons: Where vibrations find their twist

New study reveals phonon properties of β-MoB₂ single crystal

Study sheds light on the origin of elasticity in glasses and gels

New super-pure silicon chip opens path to powerful quantum computers
When injecting pure spin into chiral materials, direction matters

Physicists pioneer new quantum sensing platform

Physicists discover new way to make strange metal
Other news
A model outlining the microscopic origin of black hole entropy

Genes provide hope for the survival of Arabia's last big cat

Can coal mines be tapped for rare earth elements?

Exploring extremes in the search for life on Mars
Webb Telescope offers first glimpse of an exoplanet's interior

By listening, scientists learn how a protein folds
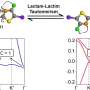
Advances in topological phase transition in organometallic lattices
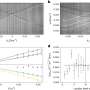
Making light 'feel' a magnetic field like an electron would