This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Novel cloud monitoring algorithm enables enhanced accuracy

Researchers led by Prof. Husi Letu from the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a novel algorithm for measuring cloud properties using neural networks.
The algorithm, known as Cloud Retrieval Algorithm based on Neural Networks (CRANN), focuses on retrieving cloud fraction and cloud-top pressure from hyperspectral measurements in the O2–O2 band. The study was published in Remote Sensing of Environment.
The CRANN algorithm is part of the broader Cloud Remote Sensing, Atmospheric Radiation and Renewal Energy Application (CARE) algorithms and is set to be integrated with China's new-generation hyperspectral instrument, the Ozone Monitoring Suite (OMS), which aims to enhance the measurement accuracy of cloud properties crucial for improving trace gas retrievals from satellite data.
The conventional methods for retrieving cloud properties have struggled with efficiency due to the higher spectral resolution and increasing spatial resolution of modern hyperspectral instruments. Existing satellite monitoring instruments like the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) and Ozone Monitoring Suite (OMS) do not capture data from the O2-A band, which complicates the use of existing retrieval algorithms like FRESCO+ and ROCINN that are specifically developed based on O2-A band observations.
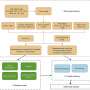
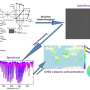
The new CRANN algorithm addresses these challenges by combining a physical radiative transfer model with a machine learning technique. The researchers trained the physics-driven neural network models using a simulated dataset generated by a radiative transfer model, achieving better performance.
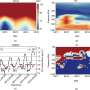
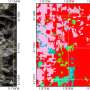
When tested against official algorithms like OMCLDO2, FRESCO+ and ROCINN, the researchers found that the CRANN model demonstrated comparable performance. For OMI and TROPOMI observations, the correlation coefficients between CRANN results and those from official algorithms were notably high, indicating strong agreement.
"The CRANN method provides a powerful tool for satellite-based cloud monitoring. It is a promising method for future atmospheric studies," said Prof. Husi Letu.
More information: Wenwu Wang et al, A novel physics-based cloud retrieval algorithm based on neural networks (CRANN) from hyperspectral measurements in the O2-O2 band, Remote Sensing of Environment (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2024.114267
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences